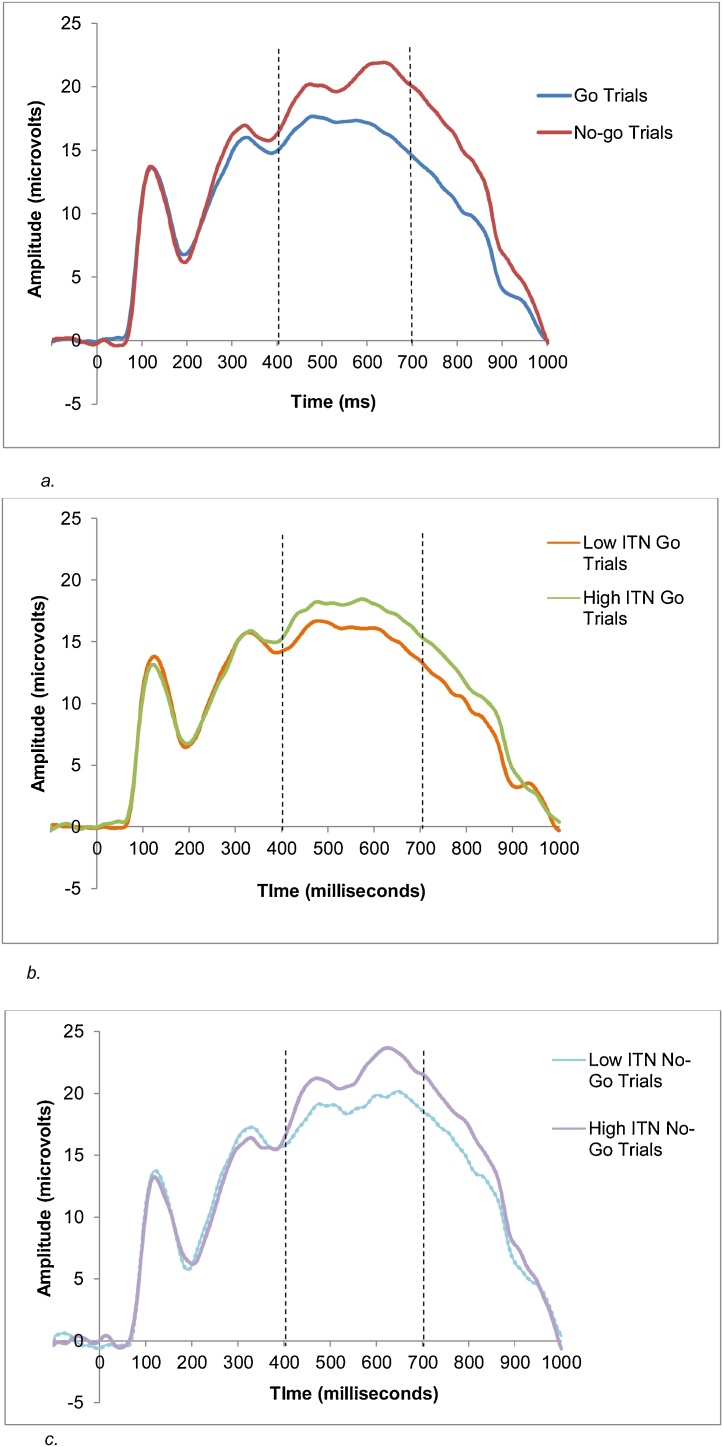
Fig. 3.
a. Grand-averaged waveform of go and no-go trials for the entire sample in the parietal region. The P3b was calculated as the mean amplitude from 400 to 700 ms (seen with the dashed lines). Four children had adjusted time windows to ensure the P3b was represented. For one child, their time window was 300–600 ms and three children had time windows of 350–650 ms. Time 0 ms indicates stimulus onset. b. Grand-averaged ERP waveforms for low and high ITN groups for go trials. The P3b was calculated as the mean amplitude from 400 to 700 ms (seen with the dashed lines). Time 0 ms indicates stimulus onset. Four children had adjusted time windows to ensure the P3b was represented. For one child, their time window was 300–600 ms and three children had time windows of 350–650 ms. Note. A median split was used to visually depict the relation between ITN and the P3b on go trials. ITN was analyzed continuously. c. Grand-averaged ERP waveforms for low and high ITN groups for no-go trials. The P3b was calculated as the mean amplitude from 400 to 700 ms (seen with the dashed lines). Time 0 ms indicates stimulus onset. Four children had adjusted time windows to ensure the P3b was represented. For one child, their time window was 300–600 ms and three children had time windows of 350–650 ms. Note. A median split was used to visually depict the relation between ITN and the P3b on no-go trials. ITN was analyzed continuously.