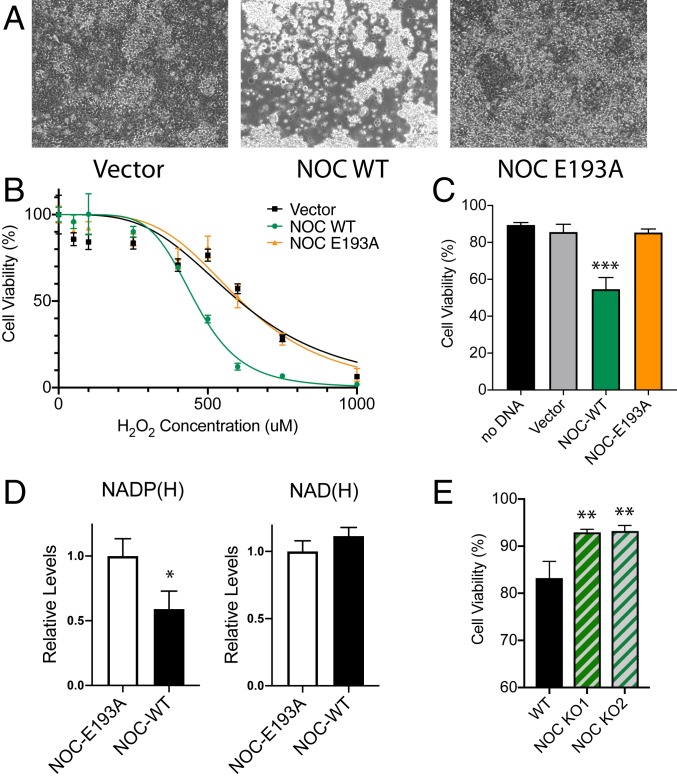
Fig. 2.
NOC regulates H2O2-induced oxidative stress response. (A) Phase contrast-microscopy images (10× objective) of HEK 293 cells transfected with a vector, mNoc-WT, or mNoc-E193A that have been treated with 500 μM of H2O2 for 24 h at 37 °C. (B) Quantification of the AquaBluer cytotoxicity assay for H2O2-treated HEK 293 cells overexpressing mNOC-WT or mNOC-E193A, plotted as a function of H2O2 concentration, n = 4. (C) Quantification of cell viability by trypan blue staining at 500-μM H2O2, n = 4 and ***P < 0.001. (D) Quantification of the levels of total NADP(H) (Left) and NAD(H) (Right) in HEK cells overexpressing mNOC-WT or mNOC-E193A, n = 3 and *P < 0.05. (E) Quantification of the cell viability by trypan blue staining for WT and two independent CRISPR-mediated Noct−/− HEK 293 cell lines that have been treated with 500 μM of H2O2 and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C, n = 3 and **P < 0.01.