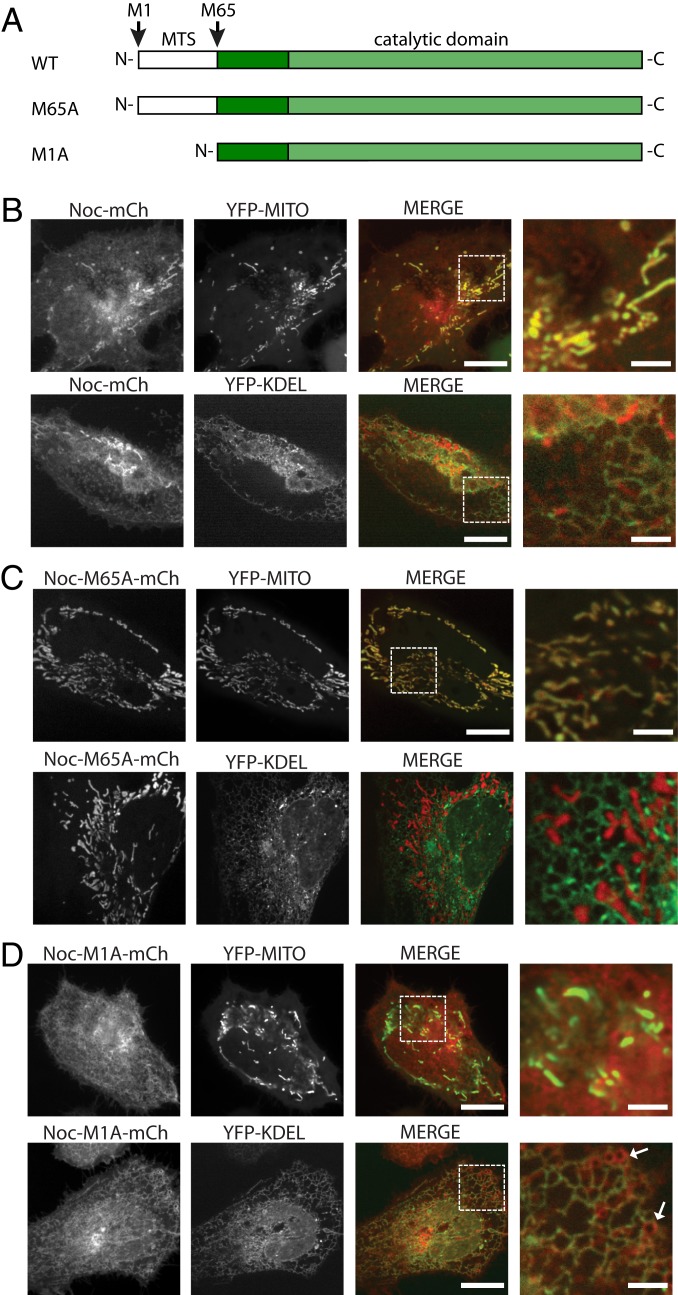
Fig. 3.
Cytoplasmic and mitochondrial isoforms of NOC are regulated by alternative translation initiation sites. (A) Cartoon representation of the coding sequences of WT and mutant NOC (mouse numbering). (B) Live-cell imaging of HeLa cells overexpressing mNOC-mCherry (shown in red) with either the YFP-MITO or the YFP-KDEL marker (shown in green). Colocalization can be seen with both markers. The rightmost column is the zoomed-in image of the area within the dotted white square in the merged column. The scale bars are 20 and 5 μM for the nonzoomed and the zoomed-in images, respectively. (C) Live-cell imaging of HeLa cells overexpressing mNOC-M1A-mCherry with either the YFP-MITO or the YFP-KDEL marker. The short isoform of NOC colocalizes with the YFP-KDEL but not the YFP-MITO marker. (D) Live-cell imaging of HeLa cells overexpressing mNOC-M65A-mCherry with either the YFP-MITO or the YFP-KDEL marker. The long isoform of NOC colocalizes with the YFP-MITO but not the YFP-KDEL marker. White arrows point to YFP-KDEL-negative membranous structures.