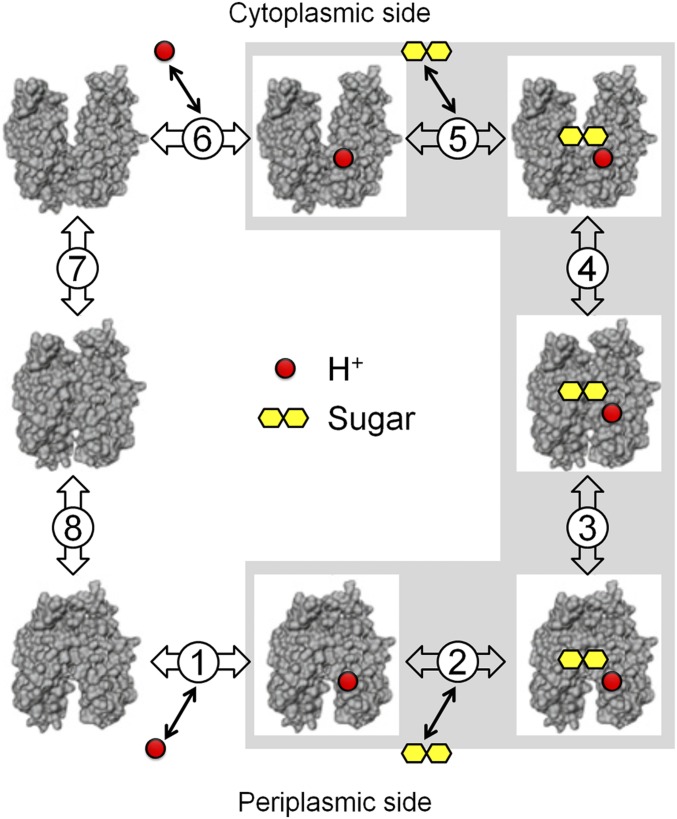
Fig. 2.
Kinetic scheme for galactoside/H+ symport, exchange, and counterflow. Symport starts with protonation of LacY (step 1 or 6 for influx or efflux, respectively), which is required for high-affinity binding of lactose. Sugar binding to protonated LacY (step 2 or 5) causes a conformational change to an occluded state (step 3 or 4), which can relax to either side where sugar dissociates first (step 2 or 5), followed by deprotonation (step 1 or 6) and return of unloaded LacY via an apo occluded intermediate (steps 7 and 8). Exchange or counterflow involves only steps 2 to 5 (gray shaded area). Since LacY catalyzes symport in both directions, when symport is in the influx direction—step 1, protonation—the pK is very alkaline (∼10.5), and step 6—deprotonation—must have a much lower pK for deprotonation to occur. However, in the efflux direction, the pK values of these steps are reversed.