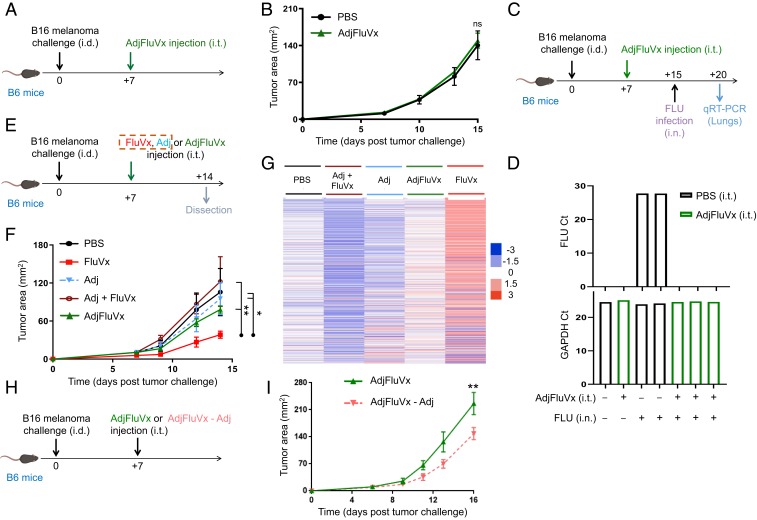
Fig. 5.
Intratumoral adjuvanted seasonal influenza vaccine administration does not reduce tumor growth but does protect against active influenza virus infection and reduces tumor growth upon removal of its adjuvant. (A) Experimental design. n = 9 to 10 mice/group. Data are representative of at least 2 independent experiments with similar results. (B) Tumor growth curves from experiment described in A. (C) Experimental design. (D) Bar graphs showing count threshold (Ct) of active influenza virus (FLU) or GAPDH control qRT-PCR transcripts from experiment described in C. (E) Experimental design. Unadjuvanted seasonal influenza vaccine (FluVx): FluVx1. n = 3 to 4 mice/group. (F) Tumor growth curves from experiment described in E. (G) Representative heatmap of NanoString PanCancer immune profiling analysis of tumors 7 d posttreatment from experiment described in E. (H) Experimental design. n = 3 mice/group. (I) Tumor growth curves from experiment described in H. ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 [2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (B and I) or Tukey correction (F)]. Error bars: mean ± SEM. i.d., intradermal; i.t., intratumoral; i.n., intranasal; AdjFluVx, adjuvanted seasonal influenza vaccine; Adj, adjuvant; Adj + FluVx, Adj added to FluVx; AdjFluVx – Adj, AdjFluVx with Adj removed.