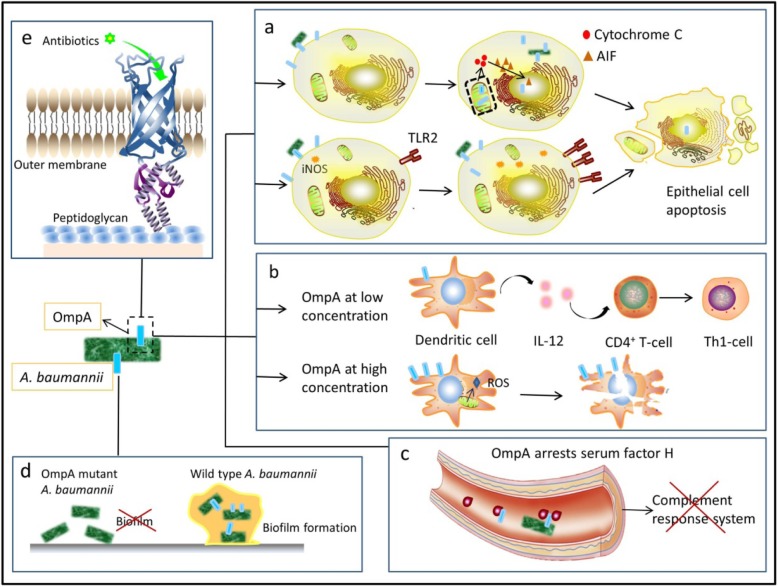
Fig. 1.
Functions of OmpA in A. baumannii. a upper panel. When contacting with epithelial cells, bacteria secrets OmpA into these cells. The OmpA are able to translocate in nucleus and mitochondria, and stimulate mitochondria to release cytochrome c. Then cytochrome c promotes apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) to translocate into nucleus and finally causes apoptosis of epithelial cells. Lower panel. OmpA increases the production of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and surface expression of Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) in epithelial cells, both of which trigger host cell death. b At low concentration, OmpA activates DCs which then stimulates CD4+T cells to exert Th1 response, while at high concentration; OmpA kills DCs by inducing mitochondria to release ROS. c AbOmpA can arrest serum factor H in serum, causing the paralysis of complement response. d AbOmpA play a dominant role in attaching abiotic surfaces and forming biofilm matrix. e AbOmpA is a porin protein which locates in outer membrane, selectively allowing the permeation of small molecular compounds