Fig. 5.
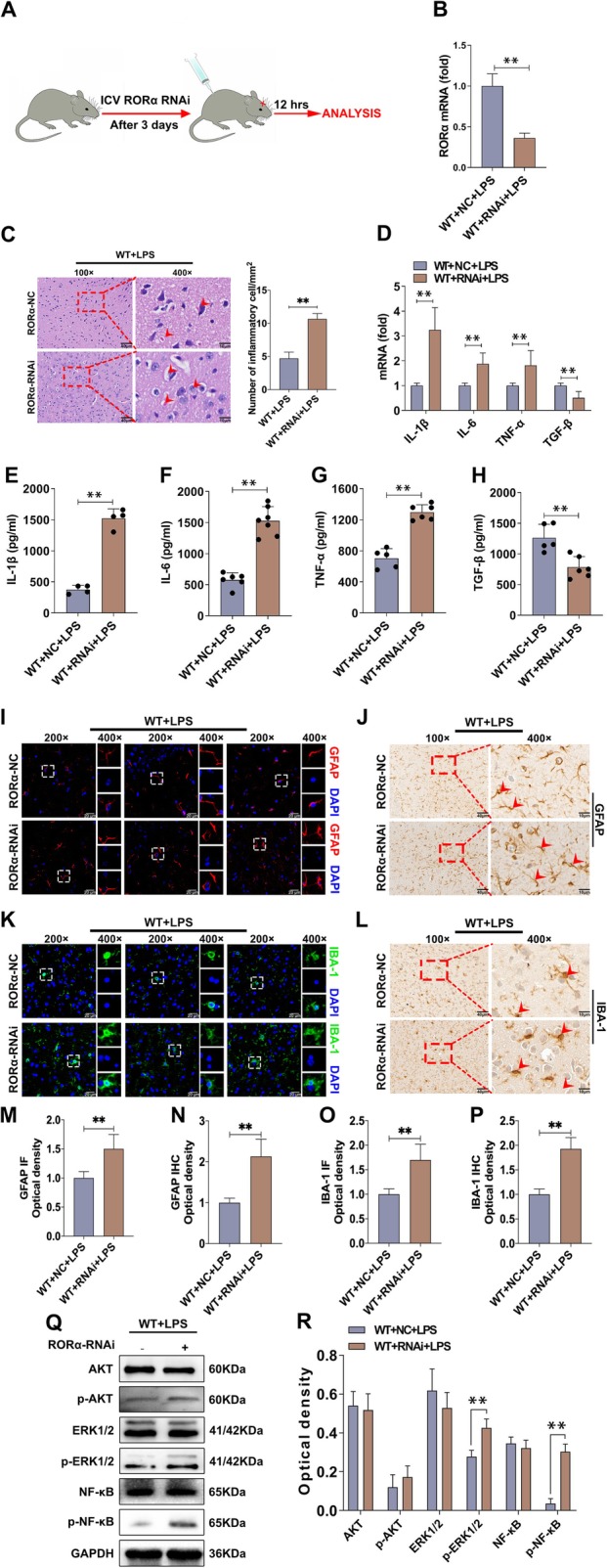
Silence of RORα aggravates the pathology and alters the NF-κB, ERK signaling pathways. a The schematic representation of the animal experiments. WT mice (n = 6 per group) were transfected with RORα RNAi or negative control (NC) RNAi through lateral ventricle. After 3 days, these mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (2.5 mg/kg of body weight). Twelve hours later, brain tissue was collected. b The expression level of RORα in brain tissue was analyzed by real-time PCR assay and calculated (n = 6 per group, t test, **P < 0.01). c The pathology of brain tissue was observed by H&E staining (n = 3 per group). Arrows in c indicate vacuolar degeneration. d The mRNA levels of cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and TGF-β) were analyzed by real-time PCR assay and calculated (n = 5, one-way ANOVA, **P < 0.01). e–h The protein levels of cytokines were analyzed by ELISA assay and calculated (n = 4, one-way ANOVA, **P < 0.01). i–p The number of astrocytes and microglia were analyzed by IF and IHC and calculated, respectively (n = 3, one-way ANOVA, **P < 0.01). q, r The protein levels of AKT, phos-AKT, ERK1/2, phos-ERK1/2, NF-κB, and phos-NF-κB were analyzed by Western blot assay and calculated (n = 3, one-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01)
