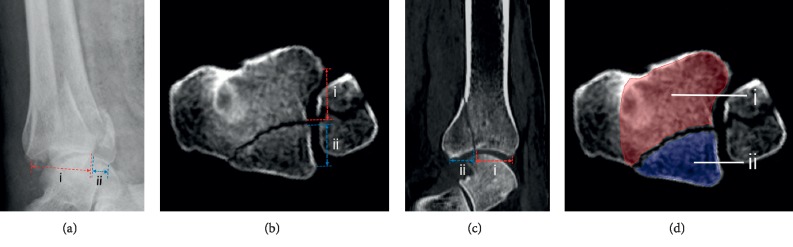
Figure 2.
Measurement of the articular involvement of posterior malleolar fractures on lateral radiographs and 2D CT images is shown. (a) Measurement on plain radiographs is shown practically. If we assume the horizontal distance between the front and back points of residual articular surface at the distal end of tibia is i and the horizontal distance between the posterior malleolar fracture line and the back point of articular surface is ii, then the percentage of involved articular surface is ii/i + ii. (b) When using axial CT linear measurement method, if we assume the distance between the front and back points of the lateral margin of residual articular surface at the level of tibial plafond is i and the distance between the posterior malleolar fracture line and the posterior point of lateral margin of the fragment is ii, then the percentage of involved articular surface is ii/i + ii. (c) When using sagittal CT linear measurement method, the process is similar to that on lateral radiographs. The percentage of involved articular surface is ii/i + ii. (d) When using axial CT plane measurement method, the boundary of the medial malleolus should be revealed at the same level. The boundary of the posterior malleolar fragment plane (ii) and residual plane (avoid medial malleolus area) (i) was delineated manually. Each area was calculated automatically by the software. Then the ratio of the involved fragment area is ii/i + ii.