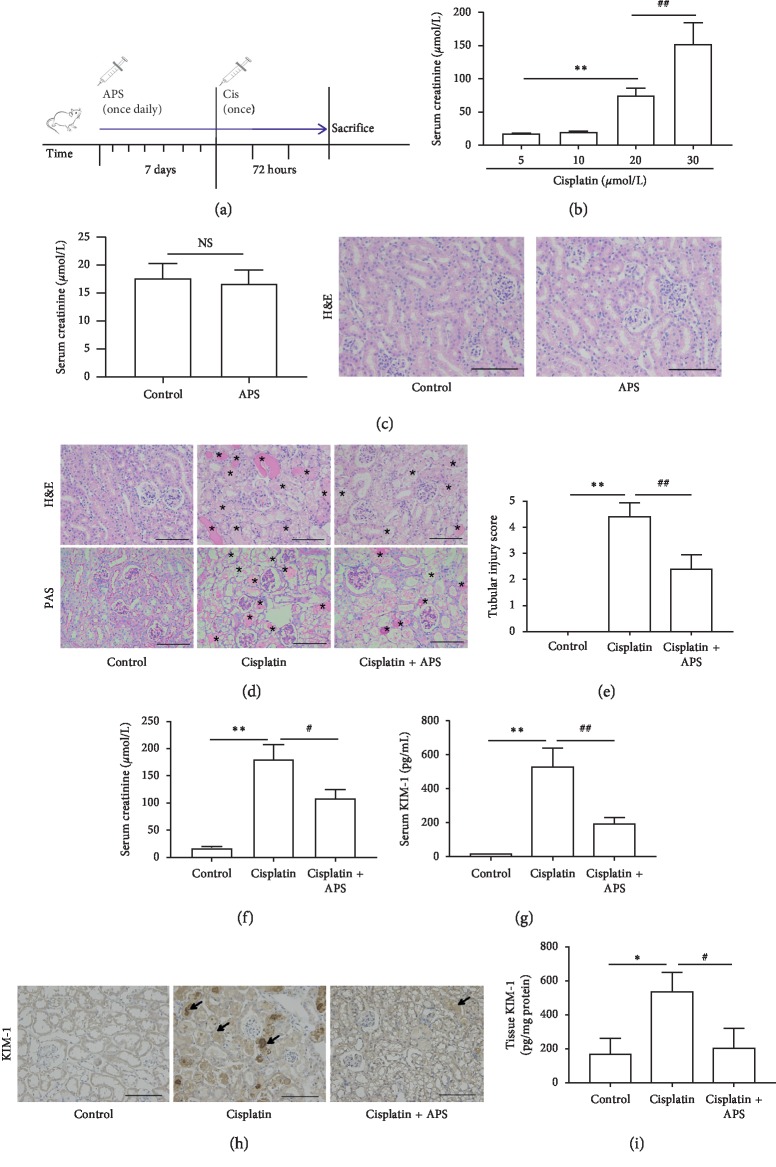
Figure 1.
APS pretreatment attenuates cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury in mice. (a) Schematic diagram of mice treated with APS and cisplatin. (b) Mice were treated with different concentrations of cisplatin. Values are means ± SEM (n = 5). ∗∗P < 0.01, cisplatin 20 mg/kg group versus cisplatin 5 mg/kg group; ##P < 0.01, cisplatin 30 mg/kg group versus cisplatin 20 mg/kg group. (c) The serum creatinine level and renal histology of mice treated with APS (30 mg/kg) for 72 h (original magnification ×200). (d) Representative images of H&E staining and PAS staining of mice kidney tissue (original magnification ×200; bar = 250 μm; ∗damaged tubules). (e) The tubular injury score is presented as means ± SEM in 5 random fields in each tissue. (f) Mice serum creatinine level. (g) Mice serum KIM-1 level. (h) Immunohistochemical staining of KIM-1 in mice kidney tissue (original magnification ×200; bar = 250 μm). (i) ELISA analysis of KIM-1 protein in mice kidney tissue. Data are means ± SEM (n = 5). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus the control group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 versus the cisplatin alone-treated group.