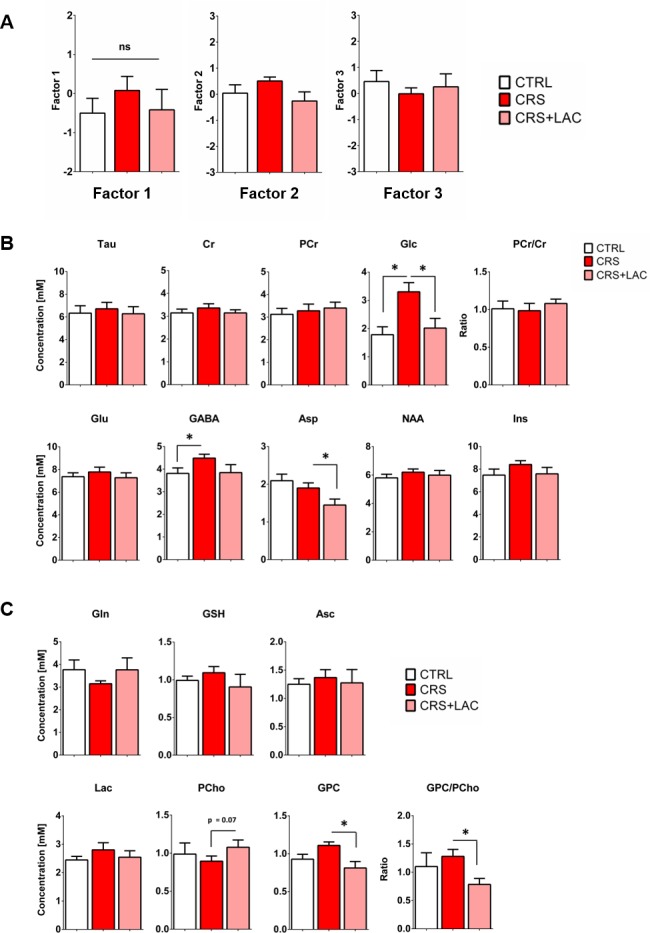
Figure 5. Effect of CRS and LAC treatment in CRS-treated mice on the accumbal neurochemical profile of high rank mice for metabolites with strong loading on Factor one.
Metabolites from Factor one with strong loading (above 0.5) include Tau, Cr, PCr, Glc, Glu, GABA, Asp, NAA and Ins. The ratio of PCr/Cr is shown as well. CRS induces a drop in Tau, Glu, PCr, Asp and NAA. Only CRS-induced reductions in Tau and PCr are restored by LAC treatment. The neurochemical profile obtained for low rank mice is reported in Figure 5—figure supplement 1. One-way ANOVA followed by LSD Fisher post-hoc test, *p<0.05, n = 5–6 per group.
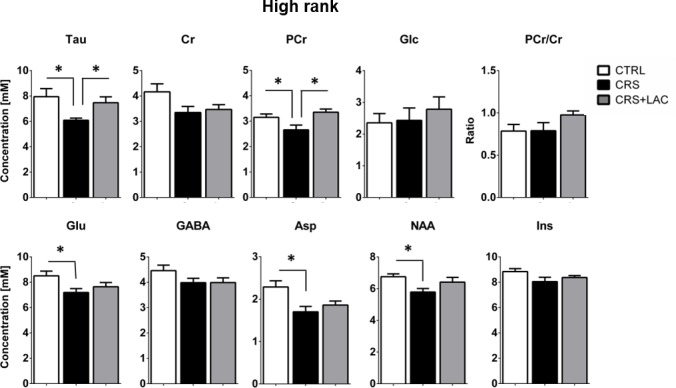
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Effect of LAC on the accumbal neurochemical profile of low rank mice after CRS.