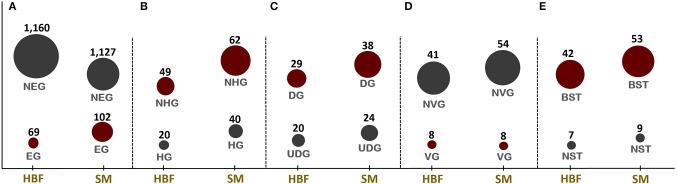
Figure 1.
Numbers of candidate drug targets predicted through in silico gene essentiality simulations in host-mimicking medium [i.e., human body fluid (HBF) and sputum-macrophage (SM)] are given in (A). The genes predicted by the HBF simulation are the subsets of SM derived results. Numbers of human non-homologous genes among essential genes are given in (B) while (C–E), respectively, give the results of the prioritization applied to the essential non-homologous genes using druggability, virulence factor, and broad-spectrum analyses. NEG, non-essential gene; EG, essential gene; NHG, non-homologous gene; HG, homologous gene; UDG, undruggable gene; DG, druggable gene; NVG, non-virulence gene; VG, virulence gene; NST, narrow-spectrum target; and BST, broad-spectrum target.