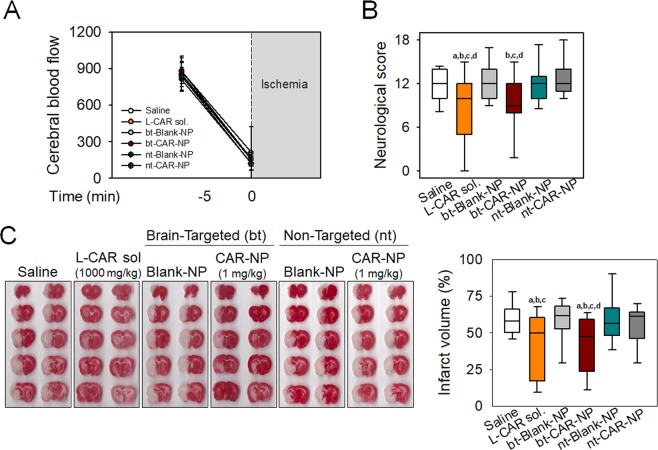
Figure 2.
Protective effects of brain-targeted polymersomes with carnosine on neurological function and infarct volume in rats with pMCAo Permanent focal ischemia was induced in rats by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAo) using intraluminal suture. Carnosine (1,000 mg/kg), bt-CAR-NP (1 mg/kg), nt-CAR-NP (1 mg/kg) or corresponding vehicles (Saline, bt-Blank-NP and nt-Blank-NP, respectively) were intravenously administered at 3 hours after ischemic onset. (A) Cerebral blood flow was monitored before and at the onset of pMCAo. Values are mean ± SD. (B) Functional deficits were examined with neurological severity scores at 24 hours after ischemia. (C) Infarct volume was calculated using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) staining of brain sections. The infarct volume for each section was determined and edema correction was performed by measurement of the infarcted and control hemisphere. Representative scanned images were shown. Box plot: median, first and third quartile; whiskers: range. All values were analyzed by one-way ANOVA. Different letters indicate a statistically significant difference (p < 0.05) between experimental groups: a vs. rats treated with saline; b vs. rats treated with bt-Blank-NP; c vs. rats treated with nt-Blank-NP; d vs. rats treated with nt-CAR-NP. A to C: N = 15 rats/group.