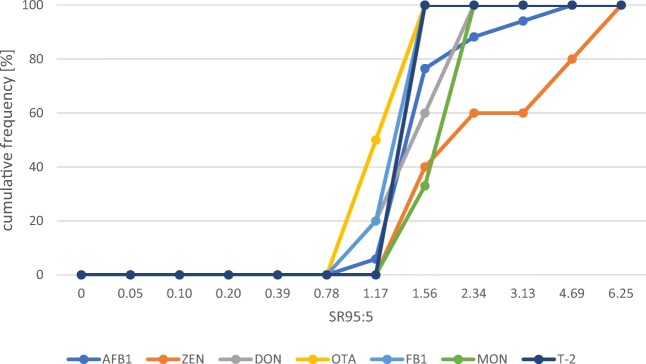
Fig. 10.
Fish species sensitivity to the different mycotoxins based on the toxicity reports from the literature listed in Annex IV and V comparing toxicity levels for AFB1 from beluga (n = 3), gibel carp (n = 3), catla (n = 4), channel catfish (n = 3), common carp (n = 7), hybrid tilapia (n = 5), rohu (n = 2), medaka (n = 2), mosquitofish (n = 2), Mozambique tilapia (n = 3), Nile tilapia (n = 31), rainbow trout (n = 39), red drum (n = 4), sea bass (n = 2), silver catfish (n = 3) and zebrafish (n = 6); for ZEN, the toxicity levels for Atlantic salmon (n = 2), common carp (n = 3), fathead minnow (n = 2), rainbow trout (n = 2) and zebrafish (n = 17) were compiled; for DON, toxicity levels for Atlantic salmon (n = 2), channel catfish (n = 2), common carp (n = 2), rainbow trout (n = 9) and zebrafish (n = 2) were used; for OTA, toxicity levels for channel catfish (n = 7), rainbow trout (n = 4), sea bass (n = 4) and zebrafish (n = 9) were compiled; for FB1, toxicity levels for channel catfish (n = 9), African catfish (n = 2), common carp (n = 4), mosquitofish (n = 2) and Nile tilapia (n = 3) were used; for MON, toxicity levels for channel catfish (n = 2), Nile tilapia (n = 3) and zebrafish (n = 2) were compared; and for T-2 toxin, the toxicity levels for channel catfish (n = 4), common carp (n = 5), rainbow trout (n = 5) and zebrafish (n = 3) were summarised; all values were calculated according to Elmegaard and Jagers op Akkerhuis (2000)