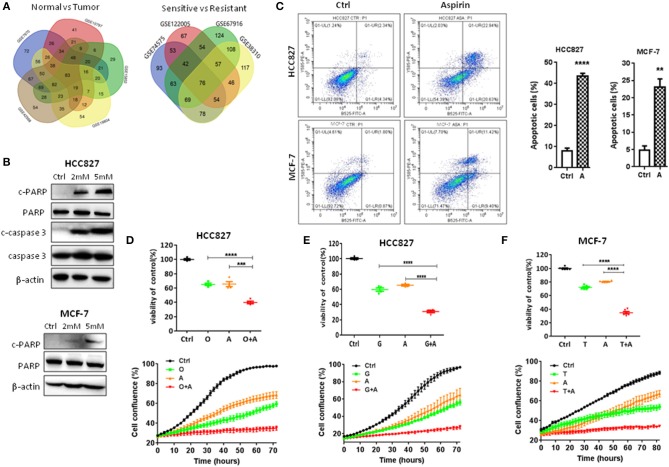
Figure 1.
Aspirin inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis of lung and breast cancer cells. (A) The Venn diagram represents the number of drugs using five data sets (GSE19804, GSE42568, GSE15852, GSE10797, and GSE7670) or four data sets (GSE74575, GSE38310, GSE67916, GSE122005) to query the CMap. (B) Western blot analysis of cleaved-caspase 3 (c-caspase 3), caspase 3, cleaved-PARP (c-PARP), and PARP in HCC827 and MCF-7 cells treated with indicated concentrations of aspirin for 72 h. β-actin was used as loading control. (C) Flow cytometry analysis of apoptosis of HCC827 treated with 2 mM aspirin and of MCF-7 cells treated with 2 mM aspirin for 72 h (left panels). Quantitative analysis of apoptotic cells identified by flow cytometry (right panels). Data were obtained from three independent experiments. (D–F) Cell viability by CCK8 assay (upper panels) and IncuCyte growth curves (lower panels) of indicated cells treated with 10 nM osimertinib (O), 10 nM gefitinib (G), 2 mM aspirin (A), 2 μM tamoxifen (T), O+A, G+A, or T+A for 72 h as indicated. The data are presented as the means ± SEM. Student's t-test was used. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.