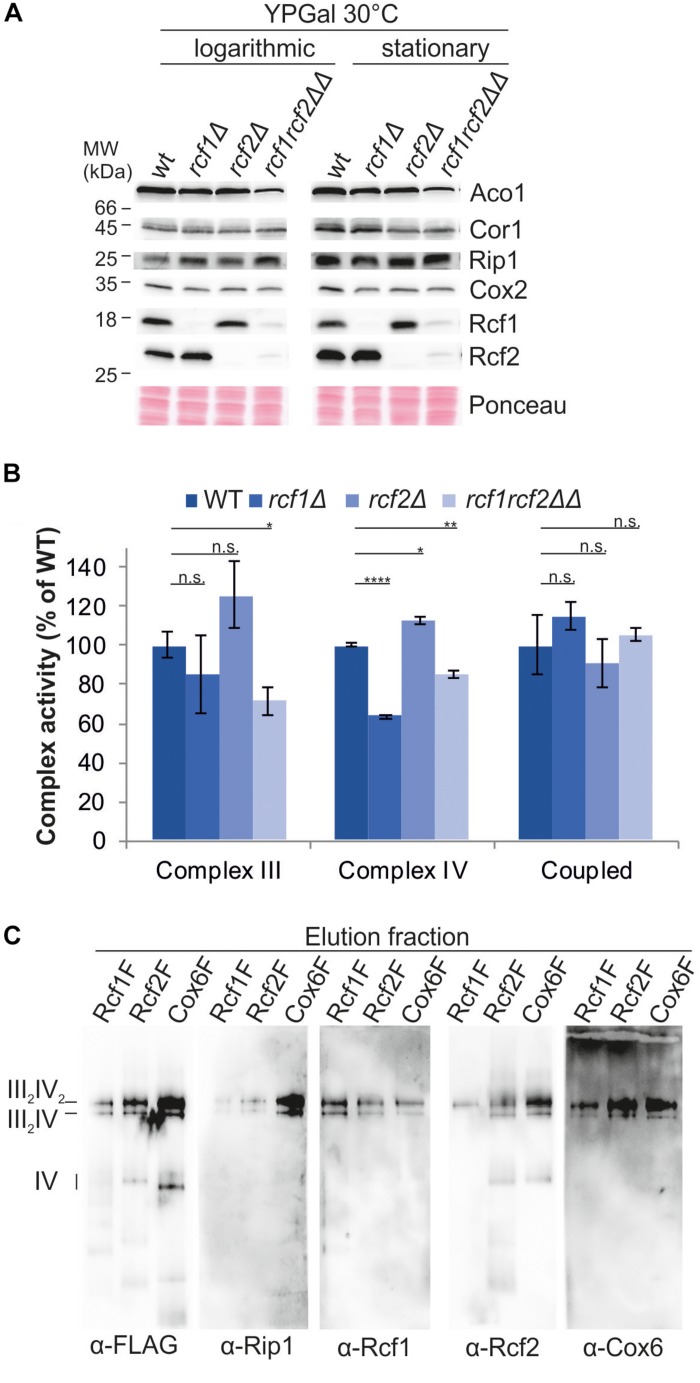
FIGURE 2.
Rcf1 and Rcf2 affect cytochrome c oxidase activity without affecting its subunit amount. (A) Steady state protein levels of cells grown to logarithmic or stationary phase showed that the loss of Rcf1 or Rcf2 did not change the protein levels of bc1 complex (Cor1, Rip1) or cytochrome c oxidase subunits (Cox2). As control aconitase (Aco1) levels and total protein amount (ponceau) were used. (B) Cytochrome c reduction measurements showed that only in absence of both Rcf1 and Rcf2 bc1 complex (Complex III) activity was decreased. Oxygen consumption measurements demonstrated that cytochrome c oxidase (Complex IV) activity was decreased upon loss of either Rcf1 or both Rcf1 and Rcf2 while loss of Rcf2 alone led to an increase in activity. The coupled activity of the supercomplexes (Coupled) was not affected by the absence of either Rcf1 or Rcf2 [the standard errors were calculated from a sample size of n = 3 (complex III and complex IV) or n = 4 (coupled)]. n.s., P > 0.05; ∗P ≤ 0.05; ∗∗P ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗P ≤ 0.001; ∗∗∗∗P ≤ 0.0001. (C) Supercomplexes were purified from mitochondria (cells grown YPG, 30°C, to logarithmic phase) via a FLAG-tag on Rcf1 (Rcf1F), Rcf2 (Rcf2F) or the cytochrome c oxidase subunit Cox6 (Cox6F). All three proteins co-purified supercomplexes but to different amounts.