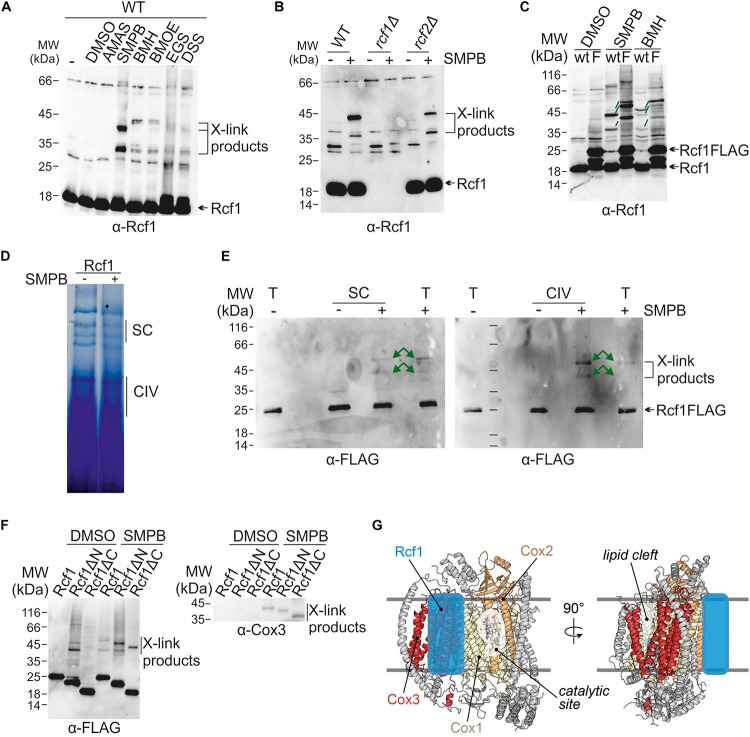
FIGURE 6.
Interaction partners and interaction sites of Rcf1. (A) Proteins in purified mitochondria were chemically crosslink followed by protein extraction, SDS-PAGE, Western blotting and immuno decoration against Rcf1. Use of different crosslink reagents (differences in reactive group and length) showed that Rcf1 has multiple interaction partners. The controls (-, DMSO) show cross reactions of the Rcf1 antiserum, which was considered during analysis in this and the following blots. (B) Chemical crosslink studies were performed as described in (A) with the crosslink reagent SMPB in the presence and absence of either Rcf1 or Rcf2 showed that the crosslink products were independent of Rcf2. (C) Chemical crosslink studies of Rcf1 or Rcf1FLAG with SMPB and BMH showed that all crosslink products of Rcf1 shift only 6 kDa (green lines), indicating that none of the crosslink products are self-crosslinks of a Rcf1 dimer. (D) Crosslinked (SMPB “+”) and non-crosslinked (SMPB “–“) mitochondria were solubilized in 2% digitonin and separated using BN-PAGE. The pattern of the supercomplexes was not affected by the crosslink. (E) As indicated in (D) gel samples containing either supercomplexes (SC) or cytochrome c oxidase (CIV) as well as total mitochondria fraction (T) were loaded on a polyacrylamide gel followed by transfer to a nitrocellulose membrane and immuno decoration. The crosslink pattern shows the same crosslink products in supercomplexes as in cytochrome c oxidase (green arrows). (F) Chemical crosslink studies with SMPB (DMSO as control) using the truncation mutants show interactions of both N- and C-termini with Cox3. The antibody against the FLAG-peptide showed unspecific binding in the control (DMSO), which was considered during analysis. (G) Model of Rcf1 binding to Cox3 of cytochrome c oxidase (adapted from PDB ID: 6HU9). We propose that Rcf1 either directly modulates the active site in Cox1, which is adjacent to Cox3, or Rcf1 modulates the lipid cleft and, thus, the active site through interaction with TM helices of Cox3.