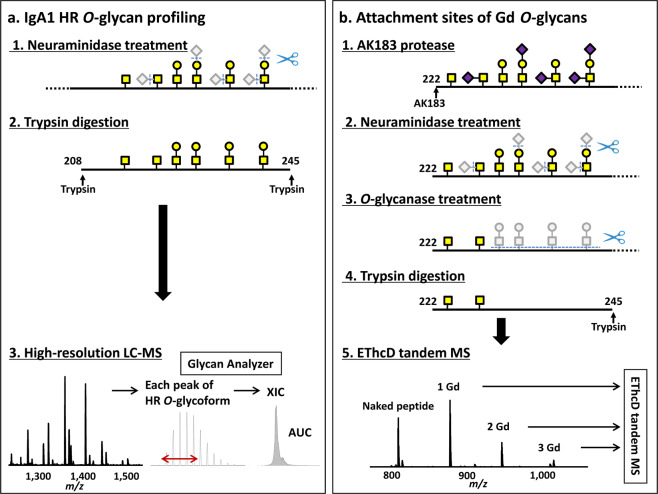
Figure 2.
New workflow for IgA1 O-glycomic analysis by using the sequential deglycosylation protocol. (a) Protocol for the profiling of IgA1 HR O-glycans. Neuraminidase treatment reduces the types of O-glycan structures from six to two (disaccharide N-acetylgalactosamine [GalNAc]-galactose [Gal] and monosaccharide GalNAc). LC-MS spectrum contains several mass peaks of HR with O-glycans, according to the number of the attached GalNAc and Gal residues. An extracted ion chromatogram (XIC) is generated for each peak and the area under the curve (AUC) of XIC of each O-glycopeptide is determined and used to calculate the relative abundance (RA) of each O-glycoform (RA = percent of total XIC of O-glycoforms detected). (b) Protocol for the analysis of the attachment sites of galactose-deficient (Gd) O-glycan. IgA1 proteins were treated with an IgA-specific protease from Clostridium ramosum AK183. After a sequential enzymatic deglycosylation with neuraminidase and O-glycanase, that ultimately leaves only Gd O-glycans (i.e., GalNAc) attached to the amino-acid backbone, IgA1 is digested by trypsin. Precursor ions corresponding to HR with one to three Gd O-glycans are analyzed by LC-tandem MS with ETD combined with supplemental higher energy collision dissociation (HCD) activation (EThcD) to assign the attachment sites of Gd O-glycans.