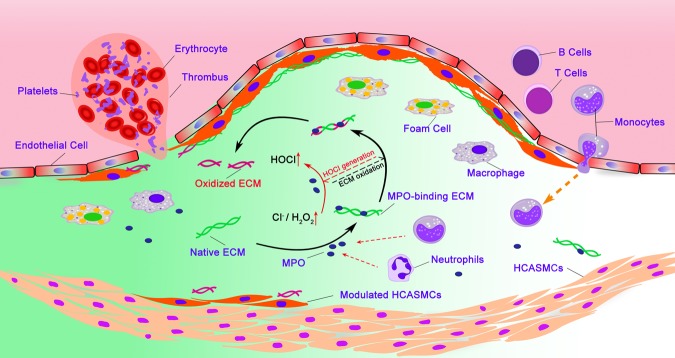
Figure 10.
Diagram summarizing proposed mechanism by which MPO induces matrix oxidation and its contributions to the generation of vulnerable plaques. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) released by activated leukocytes shows a high affinity for matrix proteins, with its catalytic activity remaining unchanged. Matrix-bound MPO catalyzes the reaction of H2O2 with Cl− to give HOCl, which subsequently induces oxidation of matrix proteins to which MPO is bound or closely associated. The progression of atherosclerosis enhances the concentration of H2O2 within the lesion, which facilitates the accumulation of oxidative modifications to the ECM of the lesion, increasing the susceptibility of the lesion to further damage and rupture.