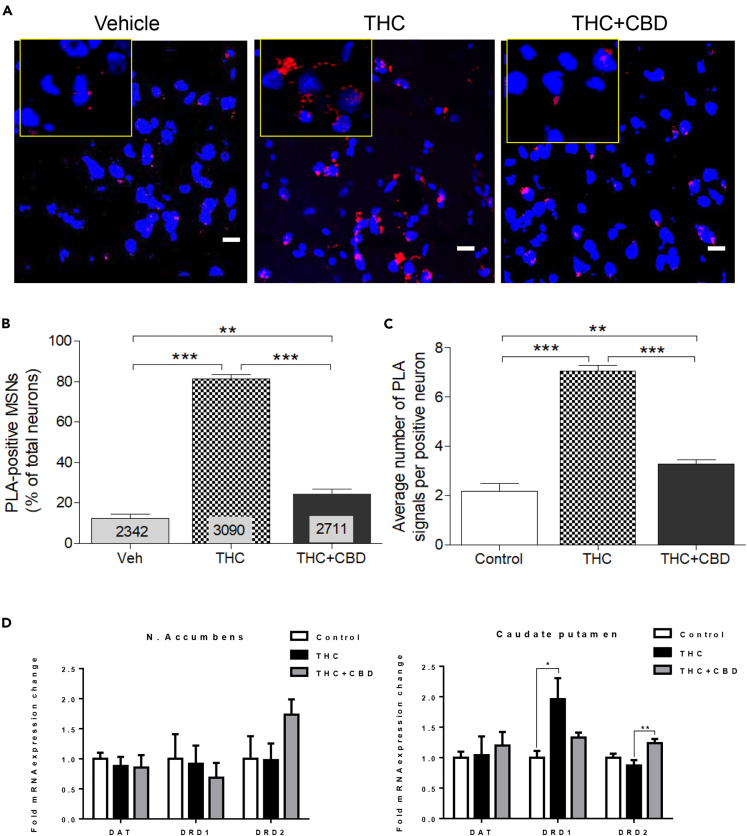
Figure 3.
Effect of Chronic THC and CBD on Dopamine D1-D2 Heteromer Expression in Monkey Caudate Nucleus
(A–C) D1-D2 heteromer expression was analyzed by PLA in the CPu of monkeys treated chronically with vehicle, THC, or THC + CBD (A). Quantification of the PLA signals (B) from the three groups of monkeys (N = 3 per group) revealed that THC increased dramatically the number of neurons expressing the D1-D2 heteromer, an effect blocked in the presence of CBD. The relative average number of heteromers per neuron was also increased (C). Results are mean ± SEM from the analysis of different slices with the number of neurons analyzed indicated. One-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni correction, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.0001. Scale bars, 10 μm.
(D) The mRNA expression of D1 receptor, D2 receptor, and DAT was analyzed in the three groups of monkeys. No changes were noticed in the NAc (left). In the CPu (right), DAT mRNA did not change, whereas THC increased D1 mRNA expression. CBD with THC blocked the increase in D1 mRNA expression and increased D2 mRNA expression. Tukey's multiple test (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).