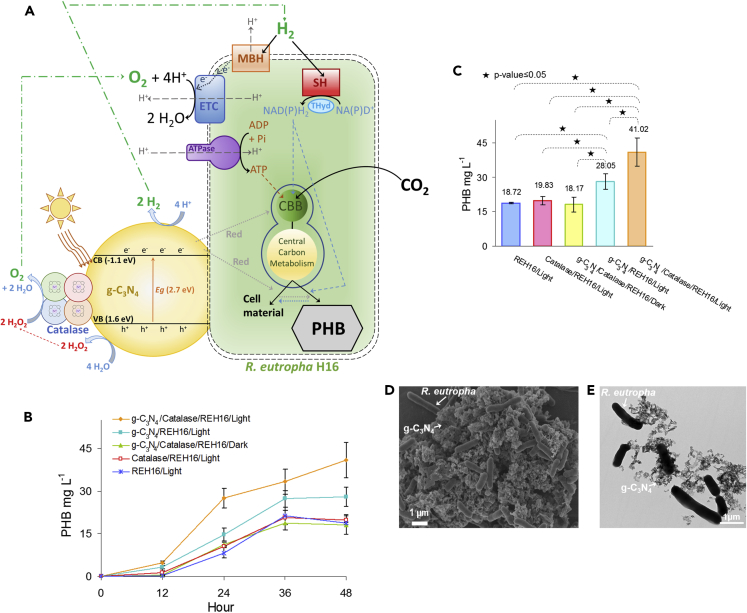
Figure 5.
Autotrophic Hybrid Photosynthesis with g-C3N4-Catalase and R. eutropha
(A) Schematic diagram of hybrid photosynthesis with g-C3N4-catalase and R. eutropha producing PHB from CO2. Water-splitting g-C3N4-catalase could augment PHB production either by increasing the quantity of H2 and/or O2 available for bacterial metabolism or by transferring unknown reducing equivalents (red) to R. eutropha. CB, conduction band; VB, valence band; ETC, electron transport chain; MBH, membrane-bound hydrogenase; SH, soluble hydrogenase; Thyd, NAD(P)+ transhydrogenase; CBB, Calvin-Benson-Bassham cycle (Brigham et al., 2013).
(B and C) (B) PHB production from CO2 over time and (C) PHB concentration after 48 h. REH16, R. eutropha H16.
(D and E) (D) Scanning and (E) transmission electron micrographs of R. eutropha grown with g-C3N4-catalase under autotrophic condition. R. eutropha cultures were grown at 30 ⁰C in minimal medium under a N2:H2:O2:CO2 (49:37:7:7) atmosphere in the presence or absence 0.5 g g-C3N4 and/or 5,000 U mL−1 bovine liver catalase. Where indicated, cultures were incubated under 4,200-lux LED light. Each curve and bar is the mean of at least three replicates with standard deviation.