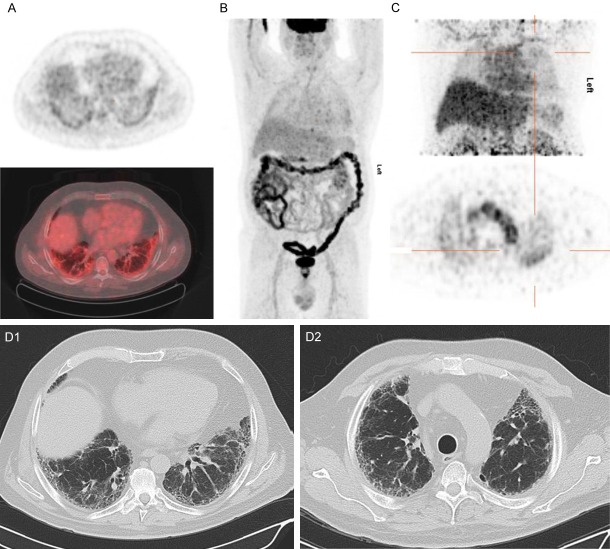
Figure 4.
[18F]FDG PET/CT and [89Zr]Zr-rituximab PET/CT of patient 2. (A) [18F]FDG PET axial views (top: PET, bottom: fusion PET/CT); (B) Maximum intensity projection of [18F]FDG PET; (C) [89Zr]Zr-rituximab PET (top: MIP image, bottom: PET); (D1 and D2) respective HRCT images of (A and C). 67-year-old male, with rheumatoid arthritis associated usual interstitial pneumonia. In the axial views of the [18F]FDG PET image (1 week before rituximab) moderate increased [18F]FDG uptake is seen in the subpleural basal pulmonary regions in some para-fibrotic areas with some honeycombing (D1), but not in the mediastinal or hilar lymph nodes. The [89Zr]Zr-rituximab PET shows mainly diffusely increased pulmonary activity. The parenchyma shows a moderately increased activity in patchy areas such as in the left upper lobe (cross hairs) this region has no honeycombing (D2). The basal subpleural regions did not show visible increased [89Zr]Zr-rituximab activity, contrast to [18F]FDG image (A). There is normal splenic activity.