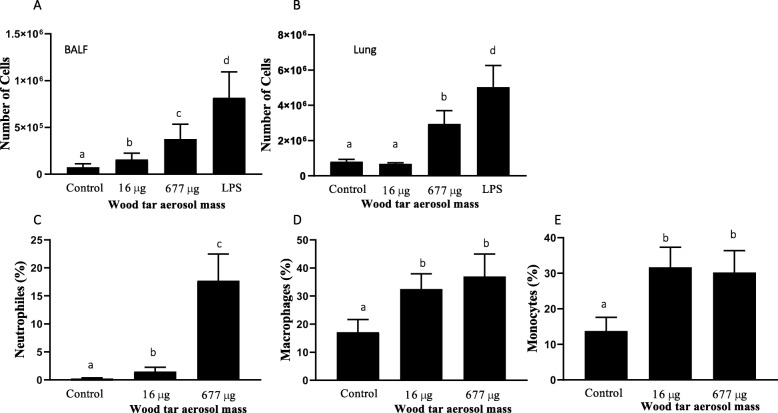
Fig. 1.
Inflammatory responses in mice following exposure to aerosols generated from water-soluble wood tar extract. Mice were exposed to wood tar solution-generated particles using an individual single exposure model. For each exposure, the initial concentration of the water-soluble extract from wood tar was 2 mg/ml or 10 mg/ml. Aerosols were generated via nebulization of these solutions and directed to six mice for each of the concentrations tested (n = 6). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was used as a positive control (n = 4). PBS was used as the negative control. a Total cell number in BALF and b total cell number in lung tissue. Further verification of the different populations was performed by flow cytometry of the collected cells stained with different markers. c Neutrophil percentage. d Macrophage percentage. e Monocyte percentage. The data are expressed as the mean ± SEM. Means marked with different letters are significantly different from each other at p < 0.05