Figure 3.
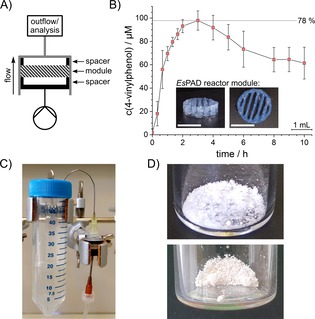
A) Schematic setup of the flow reactor for flow experiments with one reactor module. B) Conversion of p‐coumaric acid (1) in a biocatalytic flow setup employing EsPAD containing reaction modules at a constant flow rate of 12.5 μL min−1 to 4‐vinylphenol (2) quantified by HPLC in the outflow. Inset: 3D‐printed reactor modules prior to assembly into the reactor. White bar indicates 10 mm. In a reaction employing 0.125 mm substrate, conversion rates of 50–78 % were observed for more than 10 h after an initial equilibration phase. The standard deviation indicates two independent experiments. C) Flow reactor setup of one out of four parallel reactors to produce 4‐vinylphenol. The flow reactor next to the 50 mL collection tube is perfused with substrate solution by a syringe pump. For more detailed information see Figure S8. D) The purified 4‐vinylphenol (2) (top) and, after subsequent Heck‐coupling, the purified 4‐hydroxystilbene (3) (bottom) are obtained as white crystals.
