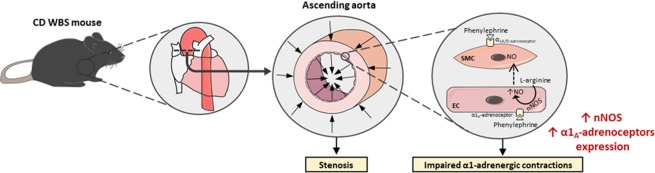
Figure 8.
Diagram illustrating the main findings of the study and the proposed mechanism involved in the observed alterations. The ascending aorta of complete deletion (CD) mice shows stenosis and attenuated phenylephrine-induced contractions compared to wild-type mice. The present study suggests that phenylephrine, besides activating α1A/D-adrenoceptors located in smooth muscle cells (SMC) to induce contraction, could also stimulate endothelial cell (EC) α1A-adrenoceptors that could trigger the release of nitric oxide (NO) by endothelial neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS)24, whose expression is increased in CD mice. This increased release of NO could be responsible for the impairment of α1-adrenoceptor-mediated contractions in the ascending aorta of CD mice. WBS, Williams-Beuren syndrome.