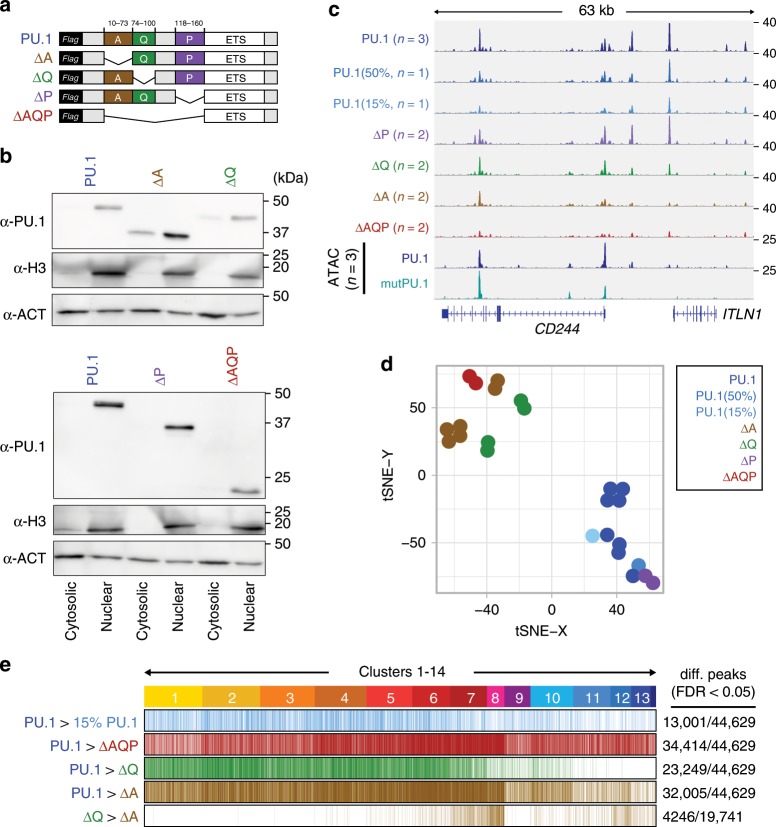
Fig. 7. Effect of PU.1 protein domains on chromatin access.
a Design of PU.1-deletion mutants. The DNA-binding domain (ETS domain) was kept in all constructs and a 3 × -FLAG-tag was added N-terminal for detection. b Immunoblot confirming the nuclear expression of PU.1-deletion mutants compared with full-length PU.1 in transfected cells using IVT mRNA. c IGV genome browser tracks of the CD84 locus showing PU.1 ChIP-seq coverage of CTV-1 cells transfected with varying amounts of PU.1 IVT mRNA as well as PU.1 mutant mRNA. ATAC-seq coverage of CTV-1 cells transfected with PU.1 (blue) and mutPU.1 (turquoise) IVT mRNA is depicted in the two bottom rows. d Two-dimensional visualization of the distribution of the indicated samples across annotated PU.1 peaks using tSNE embedding. Replicates of the same mRNA transfections are indicated by coloring. e Differential ChIP-seq peaks of WT vs. less PU.1 (15%, light blue), WT vs. ΔAQP (red), WT vs. ΔQ (green), and WT vs. ΔA (brown), as well as differential peaks between ΔQ vs. ΔA (brown) are shown across ATAC-seq-derived PU.1 peak clusters (introduced in Fig. 3). b–e Source data are provided as a Source Data file.