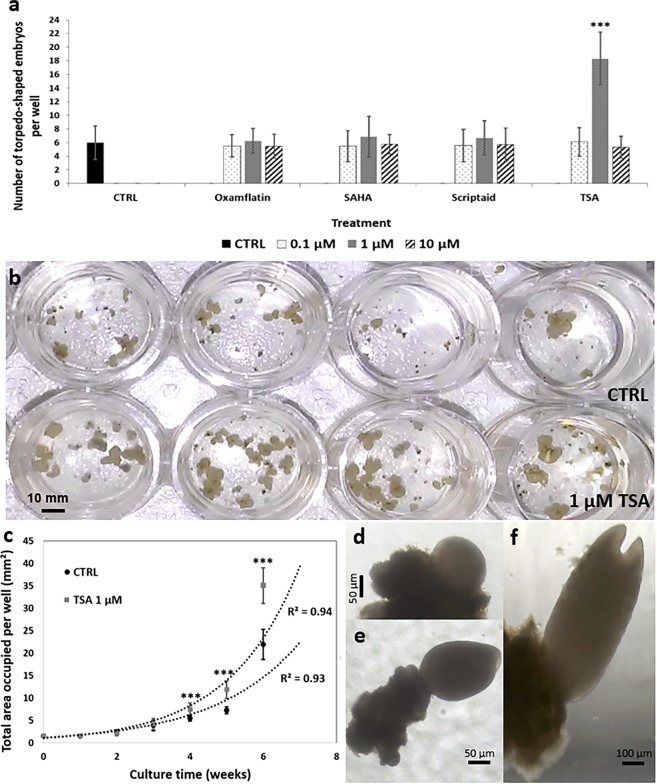
Figure 4.
Successful pilot screening of active compounds affecting SE in the automated and miniaturized system. Four compounds belonging to the HDACi family (Oxamflatin, Scriptaid, SAHA and TSA) were tested in 24-well plates at three different concentrations (0.1, 1 and 10 µM), as potential active compounds affecting C. arabica embryo differentiation. Cell clusters were exposed for 24 h to treatment before washing. (a) Embryo regeneration was scored after 9 weeks. The “CTRL” group was untreated (control). Bars show the mean of triplicate samples (n = 18 wells/HDACi/concentration/replicate) and error bars represent the SD. Differences between treated clusters and the control were analysed with a one-way ANOVA test (***P < 0.001). (b) Picture showing the increased embryo yield in the wells treated with 1 µM TSA (bottom) vs control wells (top). (c) The total area occupied by cell clusters was monitored during the embryo regeneration period. Plotted values are the mean of triplicate samples (n = 18 wells/treatment/replicate) and error bars represent the SD. Differences between clusters treated with 1 µM TSA and the control were analysed with a t-test (***P < 0.001). Cell cluster growth followed an exponential trendline (R² = 0.93) up to the sixth week. (d–f) Pictures of an emerged globular-shaped, heart-shaped and torpedo-shaped embryo after 6, 7 and 8 weeks under embryo regeneration conditions, respectively.