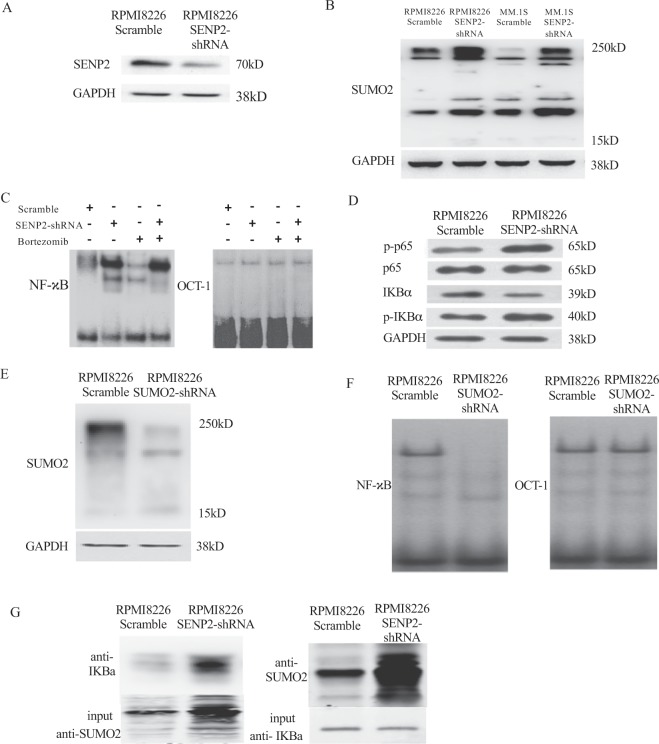
Figure 4.
SENP2 negatively regulates NF-κB activation through the modulation of IκBα sumoylation. (A) Either Scramble shRNA or SENP2-shRNA were transiently transfected in RPMI8226 cells. After 48 hours, western blot analysis was performed to detect SENP2 protein levels. Here, GAPDH serves as a loading control. (B) MM cell lines, RPMI8226 and MM.1S were transfected with either scramble shRNA or SENP2-shRNA for 48 hours, then western blot analysis was performed to detect SUMO2 protein levels. Here, GAPDH serves as a loading control. (C) EMSA assay was performed to detect NF-κB binding to its consensus binding sites on biotin labelled DNA probe using cell lysates of RPMI8226 cells transfected with either Scramble shRNA or SENP2-shRNA for 48 hours and either untreated or treated with bortezomib 25 nM. Here, OCT1 serves as an internal control for EMSA assay. (D) NF-κB activation was analysed by western blotting analysis using cell lysates of RPMI8226 cells transfected with either scramble shRNA or SENP2-shRNA for 48 hours and followed by probing with antibodies against p-p65, p65, p-IκBα and IκBα. Here, GAPDH serves as a loading control. (E) Either scramble shRNA or SUMO2-shRNA were transiently transfected in RPMI8226 cells. After 48 hours, western blot analysis was performed to detect SUMO2 protein levels. Here, GAPDH serves as a loading control. (F) EMSA assay was performed to detect NF-κB binding to its consensus binding sites on biotin labelled DNA probe using cell lysate of RPMI8226 cell lysates transfected with either Scramble shRNA or SUMO2-shRNA for 48 hours. Here, OCT1 serves as an internal control for EMSA assay. (G) Reciprocal immunoprecipitation analysis using anti-IκBα and anti-SUMO2 antibodies from cell extracts of RPMI8226 cells transfected with Scramble shRNA or SENP2-shRNA for 48 hours.