Figure 9.
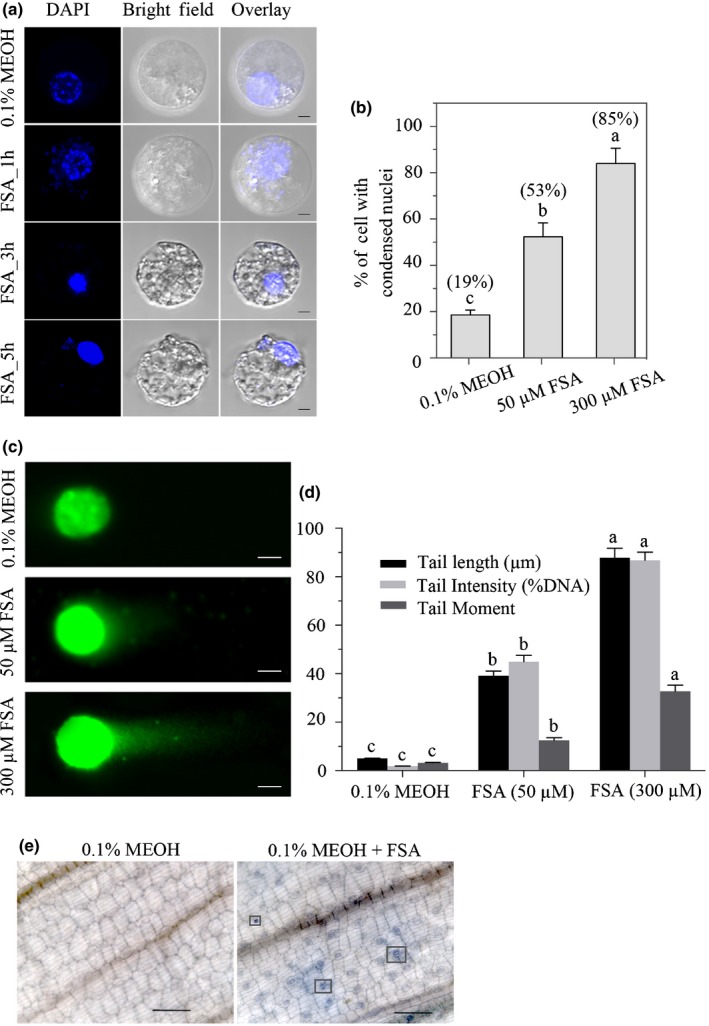
Fusaric acid (FSA) induced apoptosis symptoms in banana embryogenic cell suspension (ECS) protoplasts and leaf cells. (a) Protoplasts isolated from 7‐d‐old banana ECS were treated with 0.1% MEOH or 300 μM FSA for 24 h and stained with DAPI (nuclear marker). Images were taken by confocal laser scanning microscopy. At least 300 protoplasts were observed. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results. Bars, 10 μm. (b) Effect of FSA on the induction of nuclear condensation in banana protoplasts after 24 h of incubation. Percentages in brackets refer to the increase in protoplasts with condensed nuclei in relation to the control (0.1% MEOH). (c, d) DNA comet assay. (c) The body of banana protoplasts treated with 0.1% MEOH, 50 μM FSA and 300 μM FSA. Bars, 10 μm. (d) Changes of DNA tail length (μm), tail intensity (%) and tail moment when protoplasts treated with FSA. Data presented in (b, d) are the means ± SD from three independent experiments and different letters above the columns indicate the significant difference (P < 0.05) among different treatments at the same point. (e) Microscopic visualization of cell death on leaves treated with 0.1% MEOH, 300 μM FSA for 1 h using Trypan blue staining. Boxes indicated the death of the stomata guard cells. Bars, 100 μm.
