Figure 1.
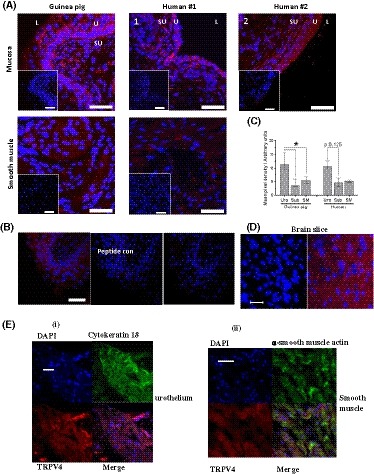
Immunohistochemical localization of TRPV4 in GP bladder tissues. A, Representative images of TRPV4 (Alomome) IHC in GP and human cryosections. TRPV4 fluorescence (red) was detected in both GP and human mucosa and smooth muscle tissue; Insets: control using only the secondary antibodies without TRPV4 primary antibody (anti‐rabbit IgG Alexa 568, life technologies). Nuclei are stained with TO‐PRO3 (Cy5; blue; Invitrogen). U, urothelium; SU, suburothelium; L, lumen. Scale bars represent 50 µm in all images. B, Representative peptide control for Alomone anti‐TRPV4 primary antibody. C, Quantitative analysis of TRPV4 fluorescence. Similar expression patterns observed in both species, with highest fluorescence in the urothelium. Median values [25%, 75%], GP urothelium and suburothelium n = 10, smooth muscle n = 7; human urothelium and suburothelium n = 4, smooth muscle n = 3, *P < .05, Wilcoxon's. D, Cerebral cortex slice TRPV4 positive control, left control with no primary Ab, right TRPV4 staining; E, Co‐staining of TRPV4 with cytokeratin 18 and ɑ‐smooth muscle actin in urothelium (i) and smooth muscle layer (ii)
