Figure 1.
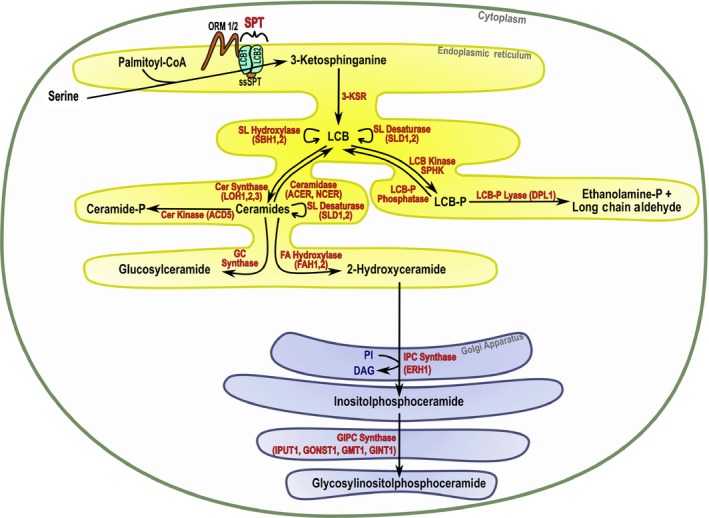
Schematic representation of the sphingolipid biosynthetic pathway in plants. 3‐KSR, 3‐ketosphinganine reductase; ACD5, accelerated cell death 5; ACER, alkaline ceramidase; Cer, ceramide; ceramide‐P, ceramide‐phosphate; CoA, coenzyme A; DAG, diacylglycerol; DPL1, dihydrosphingosine phosphate lyase; ERH1, enhancing RPW8‐mediated HR‐like cell death; FA, fatty acid; FAH, fatty acid hydroxylase; GC, glucosylceramide; GINT1, glucosamine inositol phosphorylceramide transferase 1; GIPC, glycosyl inositol phosphoceramide; GMT1, GIPC mannosyl‐transferase 1; GONST1, Golgi localized nucleotide sugar transporter 1; IPC, inositol phosphorylceramide; IPUT, inositol phosphorylceramide glucuronosyltransferase 1; LCB1,2, subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase 1 and 2; LCB, long‐chain base; LCB‐P, long‐chain base phosphate; LOH, LAG1 homolog; NCER, neutral ceramidase; ORM, orosomucoid‐like protein; PI, phosphoinositol; SBH, sphingoid base hydroxylase; SL, sphingolipid; SLD, sphingolipid Δ8 long‐chain base desaturase; SPHK, sphingosine kinase; ssSPT, small subunit of serine palmitoyl transferase; SPT, serine palmitoyl transferase.
