Figure 9.
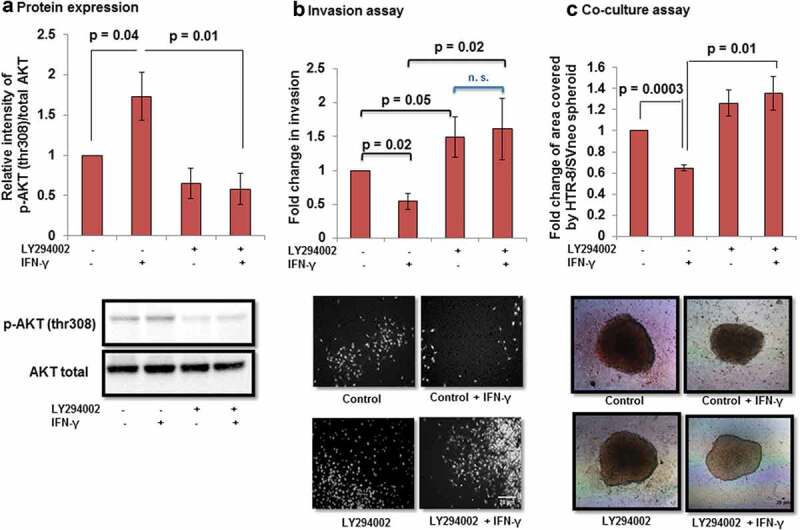
Effect of AKT inhibition by PI3K inhibitor on the invasion of HTR-8/SVneo cells treated with IFN-γ. To study the importance of AKT signaling pathway, HTR-8/SVneo cells (0.1 × 106/well) were cultured in 6-well cell culture plate overnight at 37°C in 5% CO2 and 70% relative humidity. The next day, cells were either pretreated or not pretreated with PI3K inhibitor (LY294002, 50 μM) for 2 h. Subsequently, cells were used for either Western blotting to check the expression of p-AKT (thr308) and total AKT or invasion assay in the presence and absence of IFN-γ (10 ng/mL) for 24 h. Panel a shows the densitometric plot of p-AKT (thr308) normalized with respect to total AKT. Representative blot of p-AKT (thr308) and total AKT has been appended along with Panel a. Panel b shows the fold change in the invasion of control and LY294002 pretreated cells on subsequent treatment with and without IFN-γ for 24 h. Representative images of the cells in the invasion assay has been included in Panel b. The results are expressed as mean ± SEM of fold change in the invasion with respect to control HTR-8/SVneo cells without pretreatment with LY294002 and IFN-γ treatment, observed in three independent experiments. Panel c shows fold change in the area of spreading of control HTR-8/SVneo spheroids and LY294002 pre-treated HTR-8/SVneo spheroids, respectively, with/without IFN-γ treatment for 24 h, on the monolayer of Ishikawa cells with respect to untreated control. The representative images of the spheroids are appended with Panel c. Scale bar represents 20 μm.
