Figure 4.
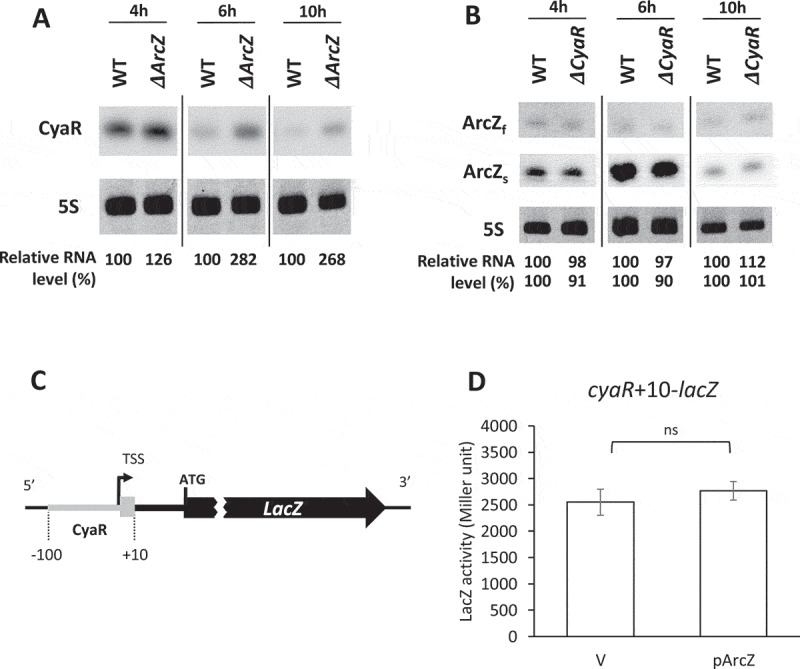
CyaR down-regulation by ArcZ. Overnight cultures of MG1655 (WT), ΔarcZ, and ΔcyaR cells were diluted 1:100 in LB medium and grown at 37°C. Aliquots of cells were sampled from the cultures at specific time intervals, and total cellular RNA was isolated. Cellular levels of CyaR and ArcZ were analysed by Northern blotting. (A) Cellular levels of CyaR were measured in WT and ΔarcZ cells during growth. CyaR was probed with an anti-CyaR oligonucleotide; 5S rRNA was detected as a loading control. (B) Cellular levels of ArcZ were measured in WT and ΔcyaR cells during growth. ArcZ was probed with an anti-ArcZ oligonucleotide; 5S rRNA was detected as a loading control. ArcZf, full-length form of ArcZ; ArcZs, short form of ArcZ. In (A) and (B), the spliced image from the same Northern blot membrane is shown with a dividing line inserted between spliced lanes. (C) Schematic representation of the cyaR-lacZ transcriptional fusion (cyaR+10-lacZ). TSS, transcription start site of CyaR. A sequence from −100 to +10 with respect to the transcription start site of CyaR was fused to lacZ mRNA. (D) Cells carrying the cyaR-lacZ transcriptional fusion were transformed with the plasmid, pArcZ, and LacZ activity was measured. Values are means ± SD; n = 3; ns, non-significant by Student’s t-test; V, vector control.
