Figure 6.
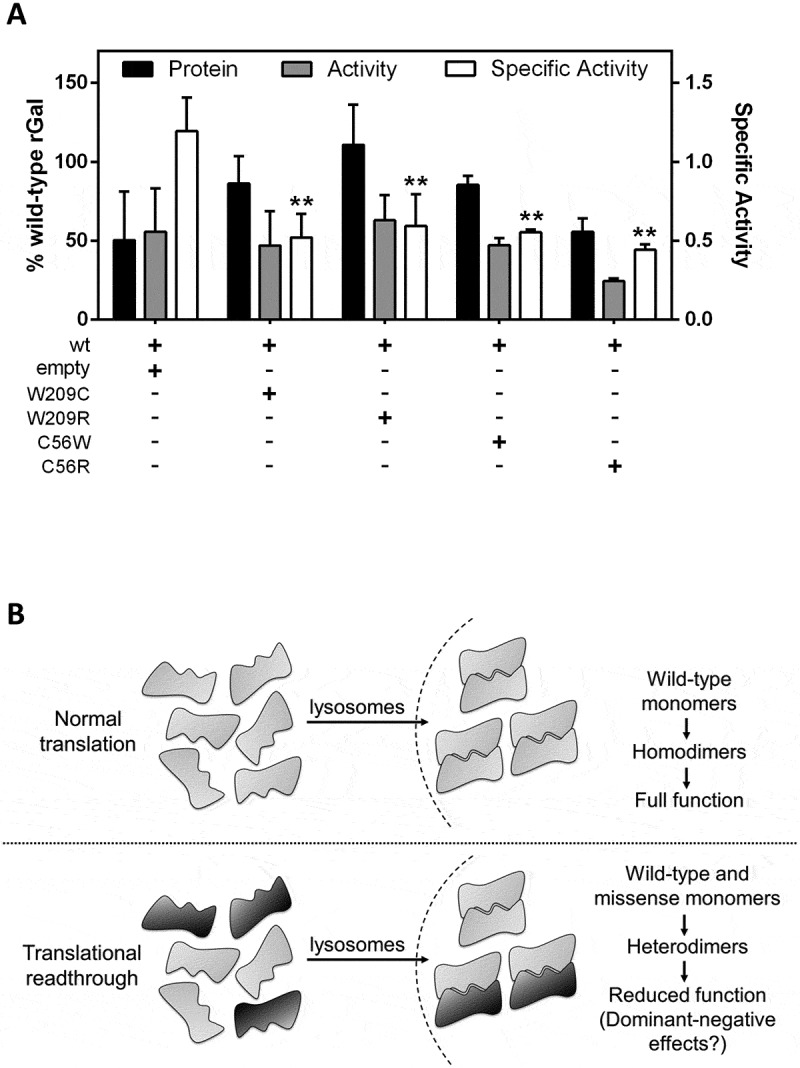
Potential dominant-negative effects of missense variants co-expressed with wild-type rGal.
(A) Co-expression studies of wild-type rGal with W209C/R or C56W/R variants. The empty plasmid was used as control. Results, indicated as % of wild-type rGal, are reported as mean ± standard deviation from three independent experiments. **, p < 0.05. (B) Schematic representation of the impact of readthrough-deriving amino acid insertions on full-length α-Gal biology. Drug-induced readthrough is predicted to result in a full-length α-Gal with wild-type features or bearing missense changes. Once transported into lysosomes, α-Gal monomers dimerize to form functional homodimers (upper panel) or heterodimers due to the interaction of monomers bearing both the original residue (grey monomer) or a missense change (black monomer) resulting in dominant-negative effects on enzyme function (lower panel).
