Figure 3.
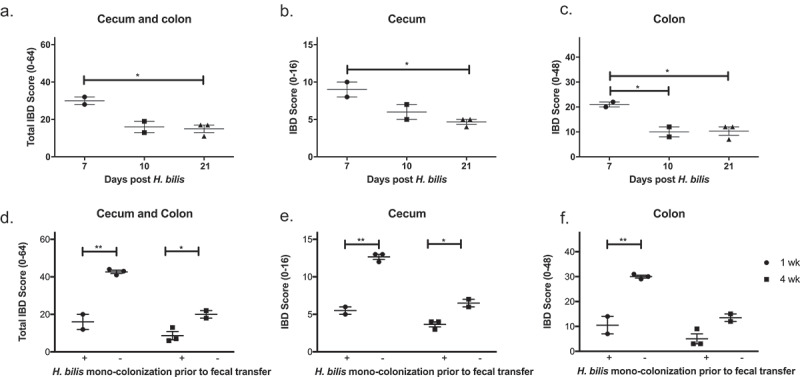
H. bilis is not a cause of IBD and prevents severe IBD in GF mice. GF Smad3+/- mice were mono-colonized with H. bilis, and the severity of inflammation was determined 7, 10 and 21 days post colonization by histological analysis of ceca and colons (a-c). IBD scores of cecum and colon (a), cecum (b), and colon (c) are shown. Possible score ranges for each tissue type are indicated on the Y-axis labels. GF Smad3+/- mice were colonized with microbiomes of mice with IBD, with or without prior H. bilis mono-colonization. The severity of IBD was determined 1 week and 4 weeks post fecal colonization by histological analysis of ceca and colons (d-f). IBD scores of cecum and colon (d), cecum (e), and colon (f) are shown. Horizontal bars represent mean ± SEM. One-way ANOVA test was performed followed by a post-hoc test of pair-wise comparisons with Bonferroni’s multiple comparison adjustment (a-c). Unpaired t-test was used for comparisons between the groups with and without mono-colonization prior to fecal transfer (D-F). *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
