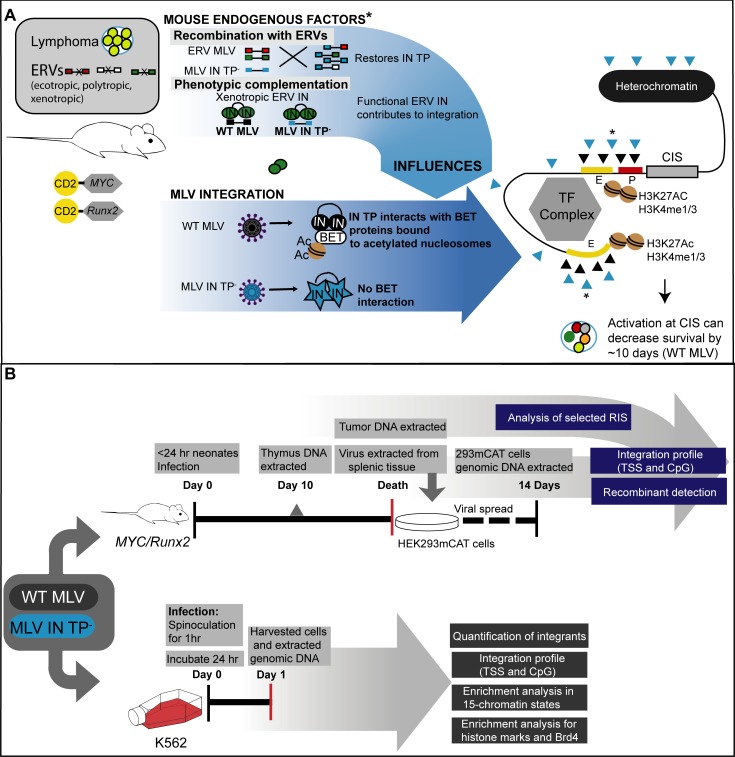
Fig 2. MYC/Runx2 mouse model and K562 cell study workflows.
(A) Overall outline of the MYC/Runx2 mouse and MLV infection. Transgenic expression of the MYC and Runx2 genes from the CD2 promoter in the C57BL6 x CBA/Ca mice results in the production of lymphomas. The mice encode endogenous retroviruses (ecotropic, polytropic and xenotropic MLVs) that can influence exogenous infecting viruses through either recombination or protein complementation if functional GagPol proteins are expressed (marked by asterisk). Infection with WT MLV (black circles) results in the IN protein interacting with host BET proteins (white oval) that bind acetylated histone marks. WT IN:BET protein interactions bias integration events (black triangles) towards promoters (P, red rectangle) and enhancers (E, yellow rectangles) through the BET nucleosome mark recognition. Integration events at known common insertions sites (CISs) result in early onset lymphomagenesis. Experiments in this manuscript examine the effects of infection of MLV IN TP- virus that has lost the interaction with the BET proteins (blue stars). Experiments map the positions of IN TP- integrations (blue triangles) with respect to promoters, enhancers, chromatin marks and known CISs in relation to the time of tumor development. (B) Schematic of experiments performed with the MYC/Runx2 mice (top) and K562 cells (bottom). Details of each experiment are found in Materials and Methods.