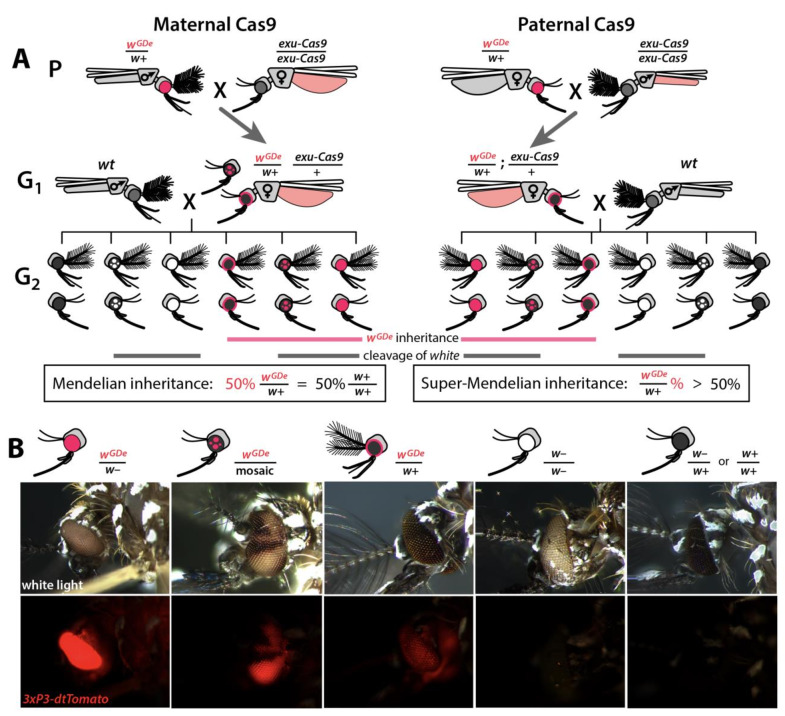
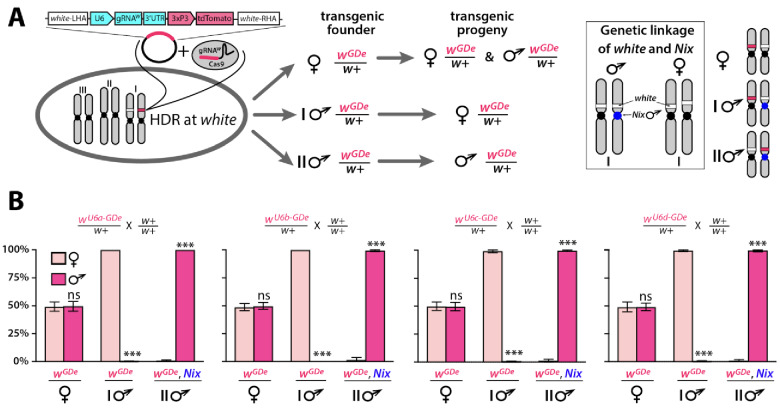
Schematic of site-specific integration and sex-linked inheritance of Gene Drive element (GDe) (
A). To direct site-specific integration of GDe inside
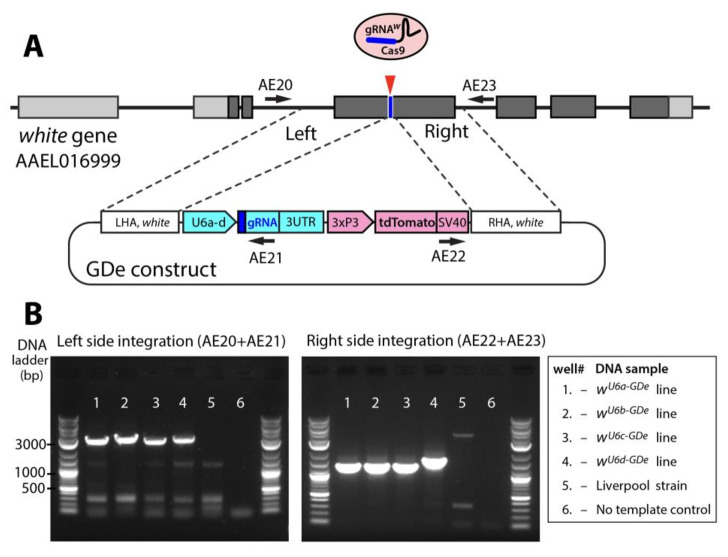
white locus (white stripe on chromosome I) via homology directed repair (HDR), wild type (
wt)
Ae. aegypti embryos were injected with a Cas9/gRNA
w complex and a plasmid carrying GDe flanked by homology regions complementary to left and right genomic regions at the
white cut site. GDe contains two genes:
U6-gRNAw to direct a site-specific cleavage and the
3xP3-tdTomato transgenesis marker (red stripe). Female mosquitoes carrying
wGDe/w+ passed
wGDe randomly to both genders, while transgenic males transmitted
wGDe either to females (type I) or males (type II) nearly exclusively. Close genetic linkage of
white and
Nix genes causes tight sex-linked inheritance of
wGDe via male founders (
B).
Nix is located near the centromere of chromosome I (
Dudchenko et al., 2017;
Matthews et al., 2018) and consequently, type I male (
♂) founders have
wGDe inserted on the chromosome copy without
Nix and therefore pass
wGDe exclusively to female progeny. On the other hand, type II male founders have
wGDe integrated on the chromosome with
Nix, and thus they transfer
wGDe and
Nix together exclusively to male progeny (box). Bars show average ± SD estimated for 20 data points. Statistical significance between gender frequencies was estimated by an equal variance
t test. (
P ≥ 0.05
ns and p<0.001***).