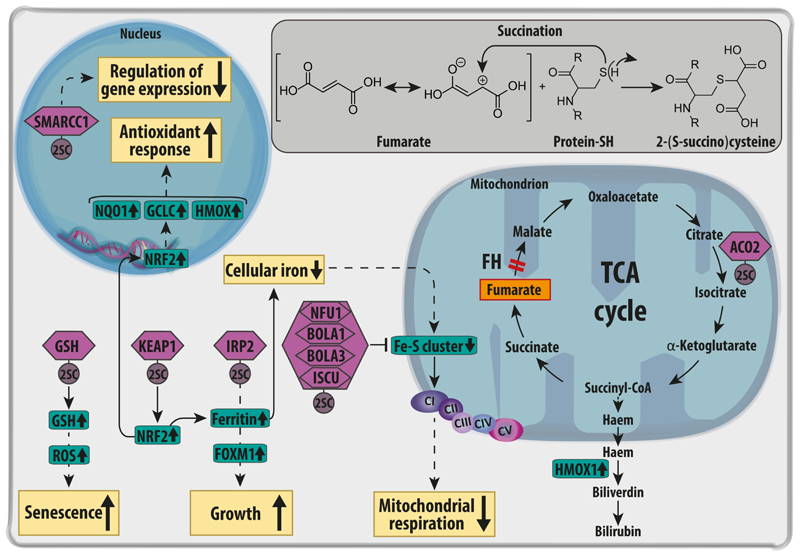
Figure 3. Targets of succination in FH-deficient cells.
Fumarate, accumulated upon FH loss, leads to a post translational modification of cysteine residues of a variety of proteins (violet hexagons) called succination. The chemical reaction between fumarate and reactive thiol residues of proteins is in depicted in the insert. Succination of KEAP1 causes the stabilisation and activation of the NRF2-mediated anti-oxidant response. One of the targets of NRF2 is Haem Oxygenase 1 (HMOX1), which is required for the haem biosynthesis and degradation pathway, an essential pathway for the survival of FH-deficient cells. Succination of Iron Responsive Element Binding Protein 2 (IRP2) inhibits the repressive function of this protein on the translation of ferritin. The subsequent increase in ferritin causes a drop in free intracellular iron. In parallel, ferritin promotes the expression of Forkhead box protein M1 (FOXM1), a pro-mitotic protein that supports cell growth. Succination of the Fe-S cluster proteins Nfu1, Bola and Iscu impairs the Fe-S clusters assembly required by the electron transport chain complex I, contributing to defects in mitochondrial respiration. The reduction of iron and the succination of key cysteine residues in its catalytic core also inactivates the TCA cycle enzyme Aconitase 2 (ACO2). In the nucleus, the succination of SWI/SNF complex protein SMARCC1 inactivates this complex, affecting gene expression and chromatin remodelling. Finally, GSH succination causes the depletion of glutathione (GSH) stores, increasing oxidative stress, and triggering senescence in primary FH-deficient cells. CI-V=electron transport chain complex I-V; KEAP1=Kelch Like ECH Associated Protein 1; Bola1-3=BolA Family Member 1-3ISCU= Iron-Sulfur Cluster Assembly Enzyme; NFU1=NFU1 Iron-Sulfur Cluster Scaffold; NRF2=Nuclear Factor, Erythroid 2 Like 2; SMARCC1=SWI/SNF Related, Matrix Associated, Actin Dependent Regulator Of Chromatin Subfamily C Member 1. GCLC: glutamate-cysteine ligase; NQO1: NADH quinone oxidase 1.