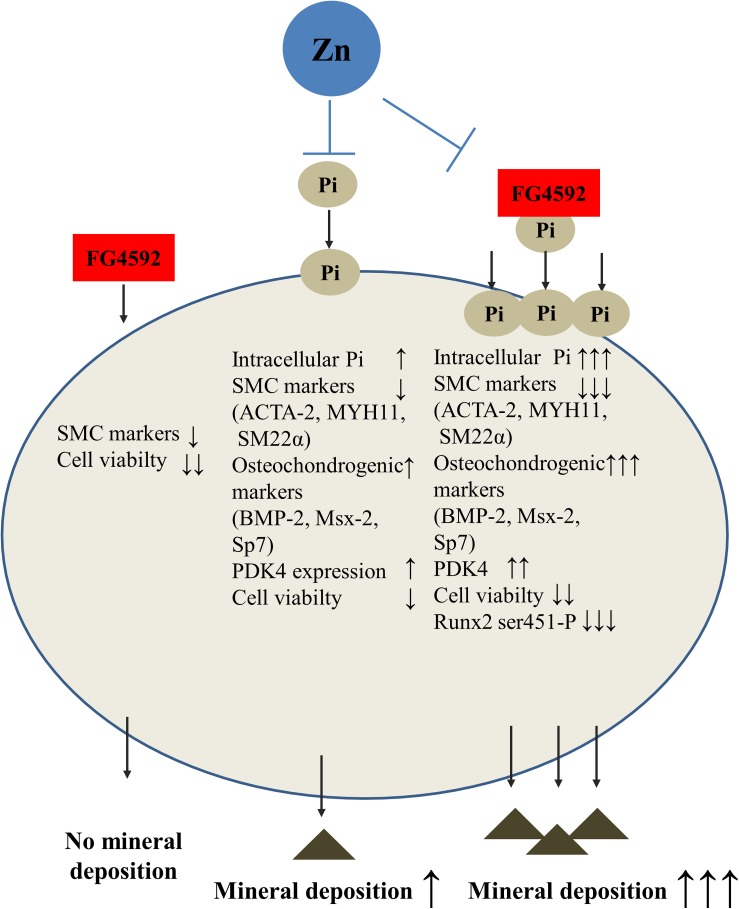
FIGURE 9.
Zinc protects against phosphate- and HIF-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor-induced vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. PHI FG4592 aggravates vascular calcification by increasing phosphate (Pi) uptake and calcium deposition by VSMCs, lowering smooth muscle-specific gene expression (ACTA-2 [smooth muscle alpha (α)-2 actin], MYH11 [smooth muscle myosin heavy chain 11], and TAGLN ([smooth muscle protein 22-α], increasing osteochondrogenic gene expression (BMP-2 [bone morphogenic protein-2], Msx-2 [Msh Homeobox 2], and SP7), inducing pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4), decreasing the phosphorylation level of Runx2 Ser451, and lowering cell viability. Importantly, zinc inhibits PHI FG4592-aggravated calcification by high Pi via maintaining VSMC phenotype, decreasing Pi uptake, lowering osteochondrogenic gene expression and the level of PDK4 as well as preserving Runx2 Ser451 phosphorylation and cell viability.