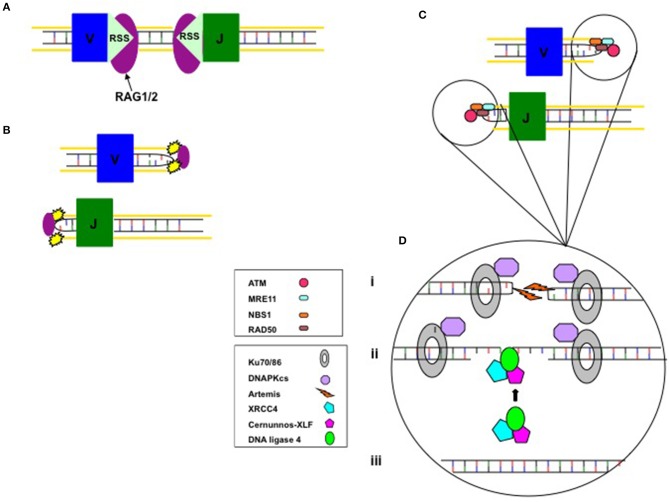
Figure 1.
DNA-DSB repair proteins and V(D)J Recombination. (A) Lymphoid cell-specific RAG1/2 proteins identify and join to the recombination signal sequences (RSS) that flank V(D)J gene segments. Site-specific DNA-DSB are introduced by the RAG proteins. (B) The covalently sealed coding sequence hairpin intermediates are bound together by the RAG complex. (C) The MRN complex binds the damaged DNA ends. ATM is activated and commences cell-cycle arrest and recruitment of the repair proteins. (D) (i) The Ku70/Ku80 heterodimer binds the coding ends and recruits DNA-PKcs to form the holoenzyme, which recruits Artemis to open the coding end hairpin intermediates by randomly nicking to generate a single-strand break with 3′ or 5′ overhangs. (ii) XRCC4, LIG4, and cernunnos-XLF co-assemble and locate to the DNA ends. The opened coding end hairpin intermediate is modified by nucleotide loss and addition of palindromic and non-templated nucleotides. (iii) Final repair and ligation by the XRCC4/DNA-LIG4/cernunnos-XLF complex. Adapted from Cowan et al. (4).