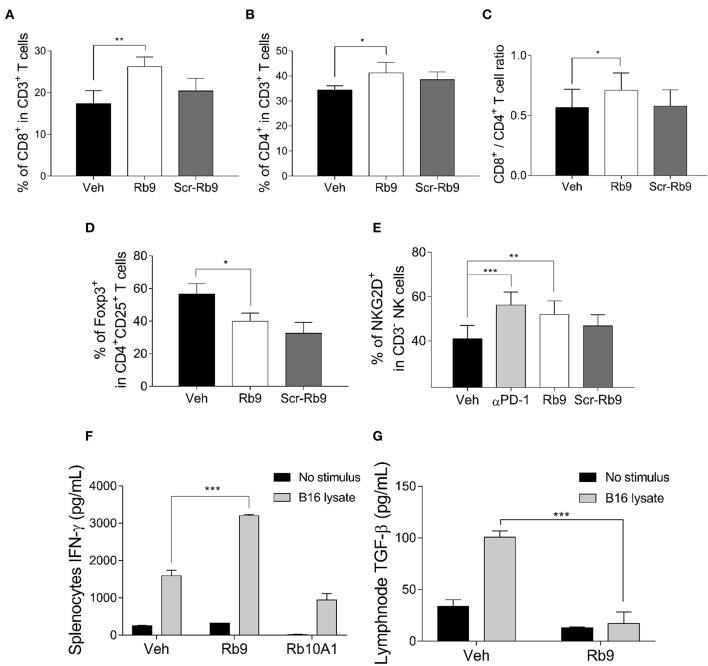
Figure 2.
Lung lymphocyte recruitment in Rb9-treated mice and specific cytokine expression in splenocytes and CD11+ lymph node cells. (A) Percent CD8+ T cells inside lungs collected after 15 days from mice receiving 200 μg of s.c. Rb9 or Scr-Rb9 for 6 alternate days starting on day 2 after challenge with B16F10-Nex2 cells; (B) Percent CD4+ T cells inside lungs as in (A); (C) Ratio of CD8+ T and CD4+ T lung infiltrates significantly increased in s.c. Rb9-treated mice. Values are means ± SEM of the previous experiments; (D) Percent CD4+, CD25+, Foxp3+ T cells inside lungs and (E) Percent CD3–NKG2D+ natural killer cells inside lungs as in (A,B). Values are ± SEM of three experiments with 4–5 pooled lungs; **p < 0.01 and *p < 0.05 with repeated measures (RM)-ANOVA and Dunnett's post-test compared to Veh. (F) Splenocytes from 17-day melanoma cell challenged mice and Rb9 or Rb10A1 i.p. treatment, for 5 alternate days, after challenge on the 1st day. The splenocytes cell culture supernatant was used to measure IFN-γ secretion after 72-h stimulus with B16F10-Nex2 lysate; (G) CD11c+ cells from cervical and axillary lymph nodes were used to measure TGF-β reduced expression on cells after 24 h with tumor lysate stimulus. Graphs from (F) to (G) represent means ± SD of triplicate experiments quantified by ELISA using standard controls. ***p < 0.001.