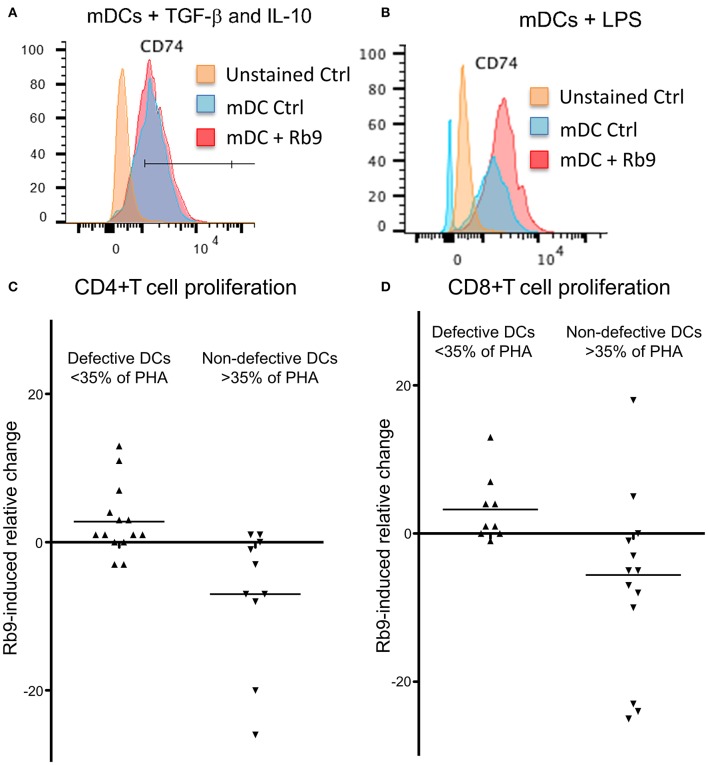
Figure 9.
Rb9 treatment of mDCs, from healthy donor and from 22 cancer patients. Ability to stimulate allogeneic lymphocytes' proliferation. Healthy donor' iDCs were stimulated to mDCs with TNF. They were also (A) simultaneously treated with TGF-β (10 ng/ml) and IL-10 (1 ng/ml) and further stimulated with Rb9 showing no change in CD74, the MIF receptor; (B) treatment with LPS and stimulation with Rb9, caused increased expression of CD74. Allogeneic CD4+ T cell (C) and CD8+ T cell (D) proliferative responses, were induced by Rb9-treatment of mDC differentiated from 22 cancer patients' PBMC. This depended on the ability of non-treated cancer patients' mDCs to stimulate T cells to proliferate: some had a poor allo-stimulatory activity (<35% the proliferation induced by phytohaemagglutinin, PHA), while others had not this same defective functional phenotype, for both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. Rb9 treatment increased the lympho-stimulatory proliferation of “defective” mDCs, but decreased the same ability in non-defective mDCs.