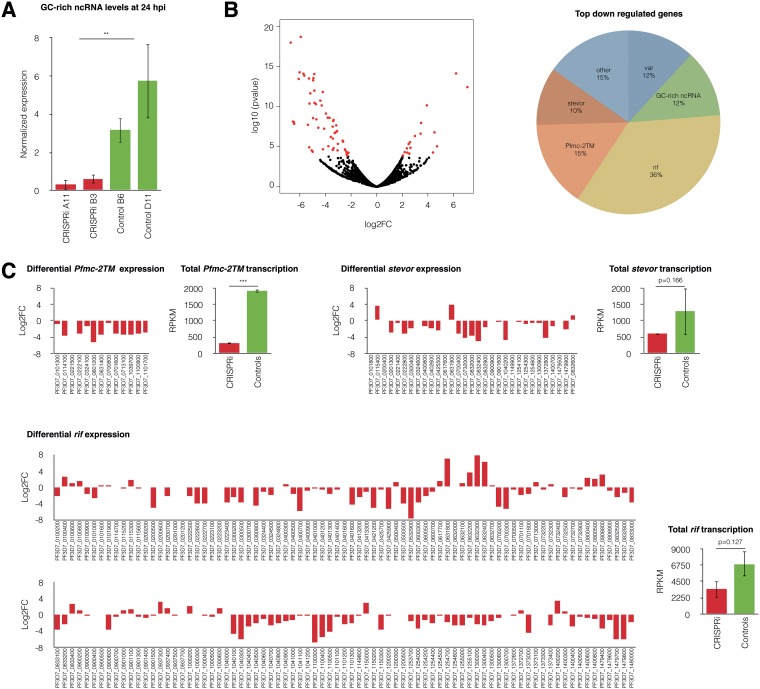
FIG 4.
GC-rich ncRNA knockdown lines exhibit downregulation of the 2TM-type supergene family. (A) GC-rich ncRNA levels at 24 hpi, as quantified by RT-qPCR, for two CRISPRi clones (B3 and A11) and two control gRNA clones (control D11 and B6). The levels of transcription were normalized to housekeeping gene fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (PF3D7_1444800) transcription levels. The means ± SEMs from three independent experiments are shown. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student's t test. **, P < 0.01. (B) (Left) Volcano plot for differential expression between CRISPRi clones and the scrambled control line. Differentially expressed genes with a 0.01 FDR cutoff are represented by red dots. The total number of significantly differentially expressed genes was 77, 77% of which were downregulated and 23% of which were upregulated. (Right) Families of top downregulated genes in CRISPRi clones significantly differentially expressed with a 0.01 FDR cutoff compared to their expression in scrambled control clones in three independent replicates. (C) (Left) Differential expression of 2TM multigene families for CRISPRi clones compared to that for the scrambled control line shows a general downregulation of most Pfmc-2TM, stevor, and rif gene family members. The log of the fold enrichment (log2 fold change [log2FC]) for three replicates of two CRISPRi clones compared to the gene expression in two scrambled control clones is represented. (Right) Mean ± SEM transcriptional levels of entire gene families, as assessed by RNA-seq, for three replicates of two CRISPRi and two scrambled control clones. Statistical significance was determined by two-tailed Student’s t test. ***, P < 0.001; **, P < 0.01.