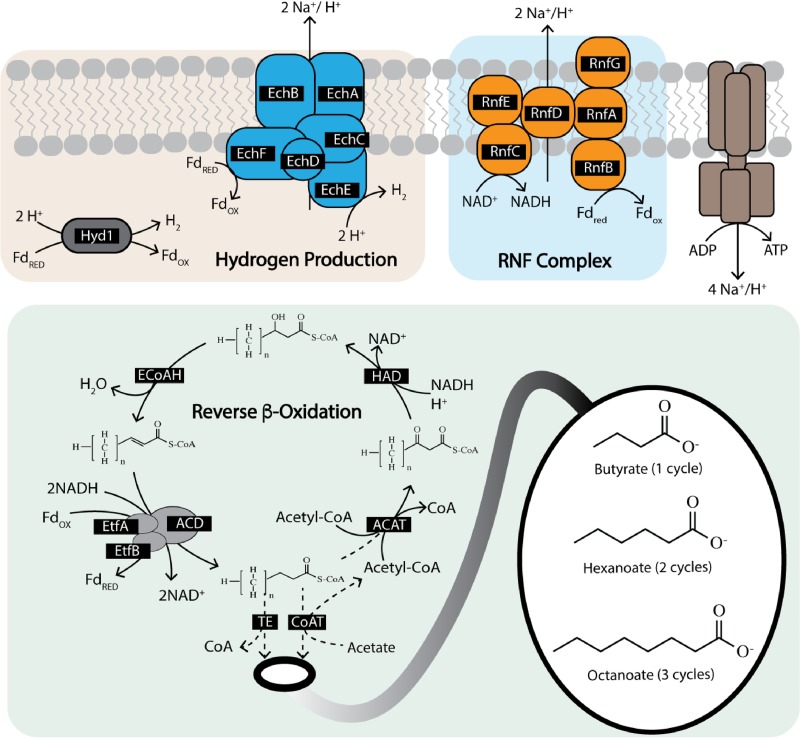
FIG 2.
Metabolic pathways involved in chain elongation. Reverse β-oxidation is a four-step process using acyl-CoA acetyltransferase (ACAT), 3-hydroxy-acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (HAD), enoyl-CoA dehydratase (ECoAH), and acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (ACD). The reduction of enoyl-CoA with NADH can be combined with the reduction of ferredoxin through an electron-bifurcating acyl-CoA dehydrogenase complex containing EtfA and EtfB. The terminal enzyme of reverse β-oxidation can be either a CoA transferase (CoAT) or thioesterase (TE). Reverse β-oxidation is coupled with proton-translocating enzymes to generate ATP with reduced ferredoxin. This figure is partly adapted from previous work (8).