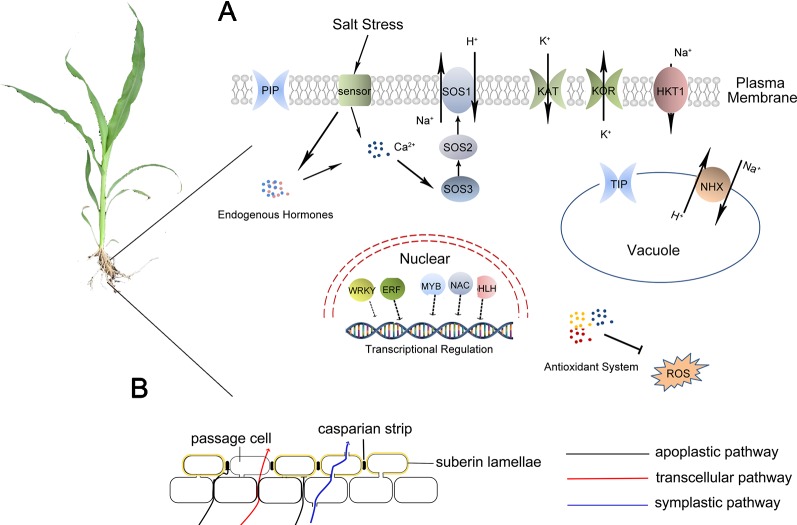
Figure 2.
Possible roles of salt resistance in sweet sorghum. (A): Cells of sweet sorghum firstly sense Na+ by an unknown sensor and change the content of intracellular hormones and Ca2+. The expression of some transcription factors, such as NAC, bHLH, MYB, is also initiated. These transcription factors then activate the expression of genes encoding proteins related to salt stress response such as SOS1, HKT1, NHX, ROS scavenging proteins, aquaporins, and some ion channels. (B): Physical barrier effect of root apoplastic barriers can block the apoplastic transpiration bypass flow of water and solutes.