Figure 1.
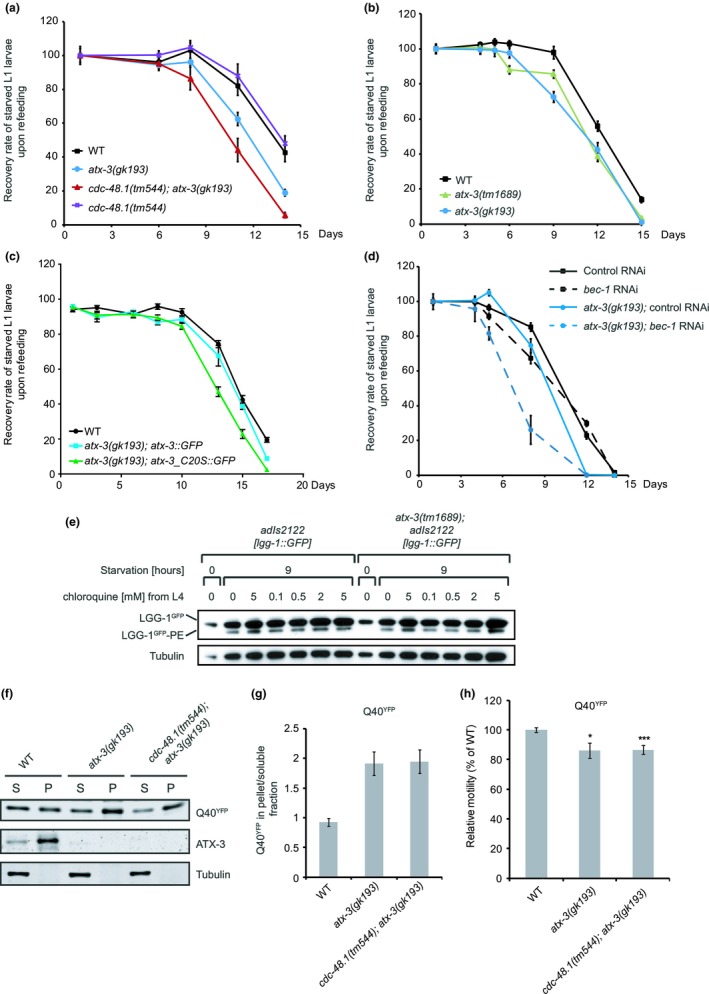
Autophagy is impaired in atx‐3 deletion worms. (a) Survival rate upon refeeding of starved L1 larvae of the long‐lived strain cdc‐48.1(tm544); atx‐3(gk193) or the single‐deletion strains atx‐3(gk193) and cdc‐48.1(tm544) compared with wild‐type worms. (b) Starved L1 larvae of the atx‐3 deletion strains atx‐3(tm1689) and atx‐3(gk193) show decreased survival rate upon refeeding compared with wild‐type worms. (c) The decreased survival of the atx‐3(gk193) mutant strain can be rescued by introduction of GFP‐tagged wild‐type ATX‐3 protein but not the catalytic inactive mutant C20S. (d) Reduction in bec‐1 levels by RNAi further decreases the survival of atx‐3(gk193) mutant worms upon starvation. (e) Western blot analysis of autophagy protein LGG‐1 in total worm lysates of day 1 adult well‐fed worms or worms starved for 9 hr. Worms were treated with the lysosomal inhibitor chloroquine at the indicated concentration from L4 stage (performed in duplicates for treatment with 5 mM chloroquine). Immunoblotting was performed using anti‐GFP and anti‐tubulin antibodies. (f) Total worm lysates of mutant and wild‐type worms expressing Q40‐YFP aggregation‐prone protein in body‐wall muscle cells have been subjected to Western blot analysis. The Western blot shows the amounts of Q40::YFP and ATX‐3 protein in the PBS‐soluble (S) and PBS‐insoluble (pellet, P; only dissolved in SDS‐containing buffer) fraction of total worm lysates in WT, atx‐3(gk193), and cdc‐48.1(tm1544); atx‐3(gk193) mutants. Western blot analysis was done using anti‐GFP and anti‐ATX‐3 antibodies. (g) Quantification of relative band intensities of Q40‐YFP in soluble and pellet fraction was done. Data are presented as mean value and SD derived from two independent experiments. (h) Relative motility of indicated strains expressing aggregation‐prone Q40‐YFP protein in body‐wall muscle cells (Student's t test, unpaired, two‐tailed, n ≥ 20, *p ≤ .05, ***p ≤ .001)
