Figure 4.
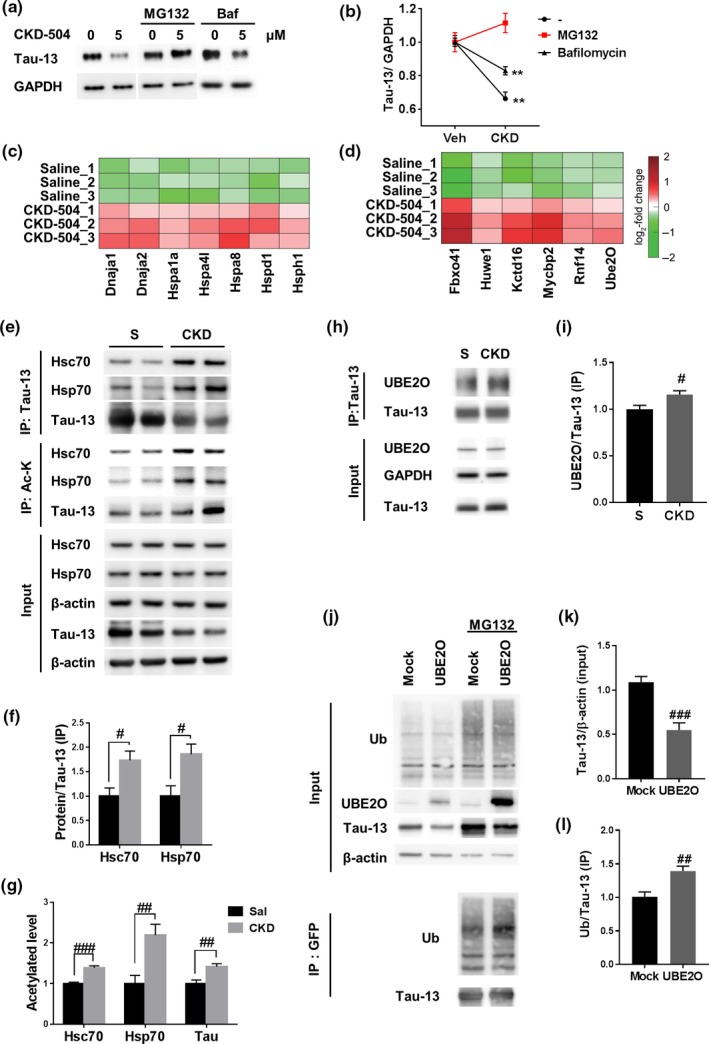
CKD‐504 potentiated proteasomal degradation of tau by changing tau protein interactome to chaperone network proteins such as heat shock proteins and E3 ligases. (a, b) Degradation of tau by CKD‐504 is mediated by proteasomal degradation in AD patient‐derived brain organoids. Brain organoids were treated with 20 μM of MG132 or 5 nM of bafilomycin for 4 hr. Representative images (a) and quantification (b) (n = 3). (c, d) The heat map represents log2 fold changes of intensities reflecting interaction strength, which were measured by mass spectrometric analysis in CKD‐504‐treated samples relative to saline controls. The color bar shows a gradient of log2 fold changes. (e–g) CKD‐504 increased acetylation and interactions between tau and chaperones in ADLPAPT mice. Human tau and acetylated proteins were immunoprecipitated by Tau‐13 antibodies and anti‐acetyl lysine antibody‐conjugated beads, respectively. Representative images (e) and quantification (f, g) (n = 3–5). (h, i) CKD‐504 increased the interaction between tau and UBE2O in ADLPAPT mice. Human tau was immunoprecipitated by Tau‐13 antibodies (n = 4). (j‐l) UBE2O ubiquitinated and reduced tau. Tau overexpressed HT22 cells were transfected with mock or UBE2O (MG132: 5 μM, 24 hr). Representative images (j) and quantification (k, l) (n = 5, independent experiments). Data are presented as means ± SEM. One‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test. **p < .01. Student's t tests. #p < .05, ##p < .01, ###p < .001. Ac‐K, acetylated lysine; Baf, bafilomycin; CKD, CKD‐504; S, saline; Ub, ubiquitin
