Figure 2.
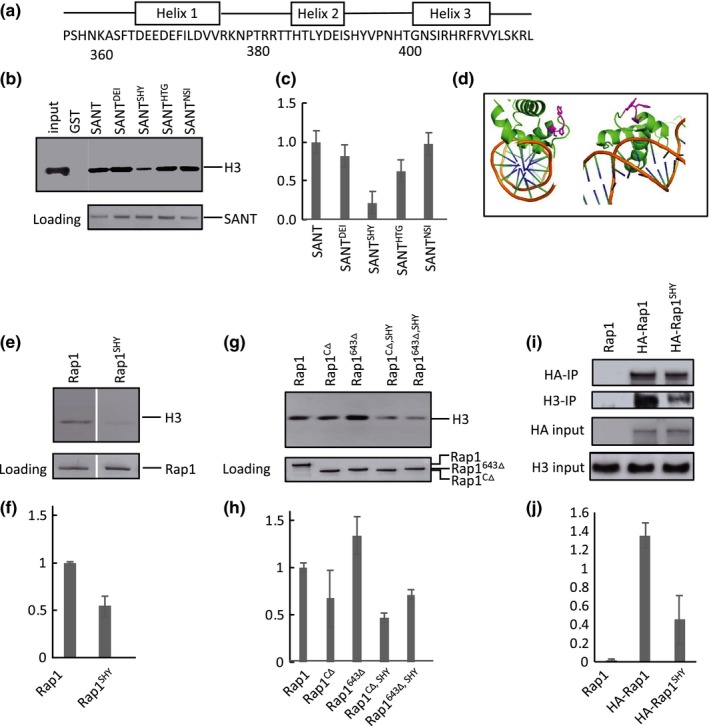
Amino acids 392–394 (SHY) facilitate Rap1‐histone interactions. (a) Location of alpha‐helices within the SANT domain, redrawn from Konig et al. (1996). Triple alanine mutants were generated from amino acids 359–410. (b) Immunoblot analysis of in vitro GST pull‐down assay of histones showing representative triple alanine mutants. Pull‐down was performed with equimolar GST‐SANT (0.5 μM) and histones (0.5 μM) at 400 mM NaCl. Bottom panel is the blot stained with Ponceau S as a loading control. (c) Quantitation of triple alanine mutants binding to H3/H4, normalized to Ponceau stain signal, and with WT SANT set to 1.0. Error bars for all quantitations indicate standard error of the mean (N = 2). Only mutant 12 (amino acids 392–394, SHY) showed a significant loss of H3 signal. (d) Two views of the SANT domain bound to DNA. Amino acids SHY side chains are colored in magenta. SHY is located immediately C‐terminal to helix 2, with side chains facing away from the Rap1‐DNA interaction surface. Image generated using Pymol (PDB ID: 3UKG). (e) Representative immunoblot analysis of GST pull‐down histone binding assay with full‐length Rap1 and Rap1SHY. Pull‐down was performed with 0.5 μM each Rap1 and H3/H4 at 400 mM NaCl. Rap1SHY displays a ~50% loss of histone binding. Bottom panel is a loading control gel stained with Coomassie blue. (f) Quantitation of full‐length Rap1 and Rap1SHY binding to H3/H4 (N = 3). (g) Representative immunoblot analysis of GST pull‐down histone assay using two truncated versions of Rap1 lacking the C‐terminus, Rap1CΔ and Rap1643 Δ. Pull‐down was performed with 2 μM Rap1 truncated constructs and 2 μM H3/H4 at 400 mM NaCl. Both truncated forms show a significant and similar loss of histone signal when amino acid SHY is mutated to AAA (rightmost two lanes). Bottom panel is Coomassie loading control. (h) Quantitation of g (N = 3). (i) Representative coimmunoprecipitation of histone H3 with immunoprecipitated HA‐Rap1 and HA‐Rap1SHY. Input is 5% of the WCE, and Rap1SHY shows a significant loss of histone binding in the extracts. (j) Quantitation of the ratio of co‐immunoprecipated H3 to input H3 signals in i (N = 3)
