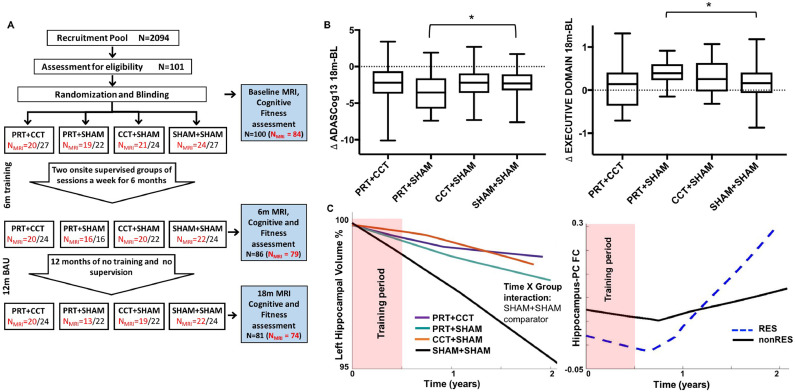
Fig. 1.
SMART Trial design and statistical models. (A) Randomization was into one of four training groups – combined progressive resistance training and computerised cognitive training (PRT+CCT), PRT and cognitive sham (PRT+SHAM), CCT and sham exercise (CCT+SHAM), sham exercise and cognitive sham, (SHAM+SHAM). MRI, cognitive and fitness assessments were carried out at baseline, directly after 6 months of training (6M) and at 18 months (18M), following a one-year usual care (UC) period with weekly telephone contact by research staff to administer health/adverse event checks in all participants. In addition, cognitive, physical, social, recreational, volunteer and religious activity participation was recorded daily for the entire 18 months in a logbook by each participant. (B) Raw change in the trial's primary outcome (ADASCog error scores) over the complete 18-month period, as well as neuropsychologically-defined Executive domain scores were compared between SHAM+SHAM and the three training groups. Box-and-Whisker plots show the median (horizontal line), interquartile range (box) and upper and lower quartiles (whiskers) of change in outcome scores for each training group. Dotted line indicates no change in outcome over the 18-month period. LME analysis found significantly (*Time x Group p < 0.05 superimposed on the Box-and-Whisker plots) improved cognition in the PRT+SHAM group compared to SHAM+SHAM on both outcomes (model including covariates age, sex and education, as well as group factor and time as continuous variable). (C) Basic Linear Mixed Effects (LME) model including baseline covariates (age, sex, education), time (as continuous variable), group (SHAM+SHAM comparator) and Time x Group interaction. Unadjusted locally-weighted mean trajectories were plotted over a sliding temporal window (i.e., lowess plot) for hippocampal volume as percentage of baseline and functional connectivity z-scores for all four groups over the 18-month trial period. Temporal relationship determined the subsequent modelled time interaction function in the LME.