Fig. 5.
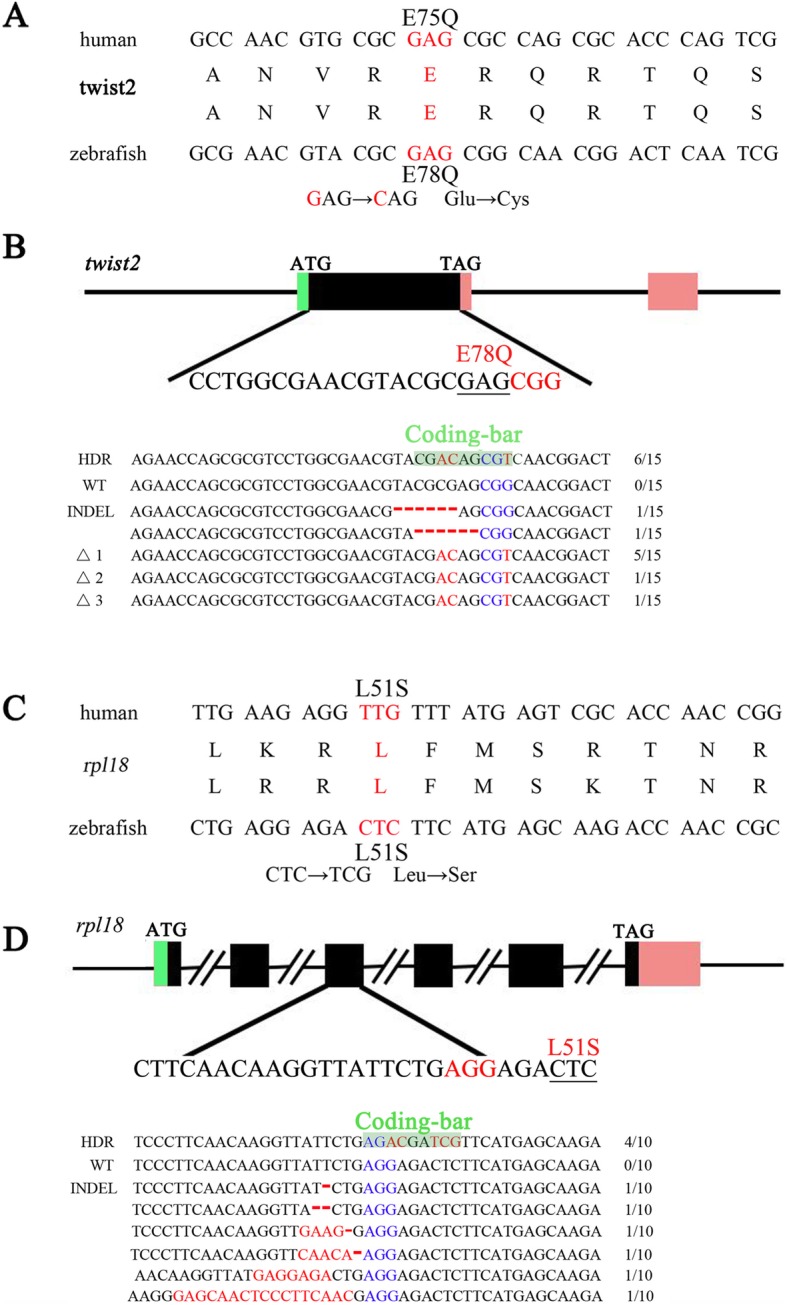
zLOST enables mimicking of human disease related mutations in zebrafish
Alignment of human patients and desired zebrafish mutations to model human Barber-Say syndrome (BSS) or Diamond-Blackfan anaemia (DBA), schematic outlines of the gene editing strategy and sequencing of the resulting twist2 and rpl18 zebrafish loci. a Diagram of the mutation associated with human BSS. The substituted target base is marked in red, which means a p.E78Q amino-acid change in the zebrafish homologue precisely mimics the p.E75Q mutation found in human patients. b and d Design principles of HDR templates that contain a non-synonymous mutation of the sequence close to the PAM site in addition to synonymous nucleotide changes that create a Coding-bar used for genotyping that utilizes a de novo endonuclease restriction site. Sequencing result at the twist2 and rpl18 zebrafish loci targeted by the zLOST system. The Coding-bar includes a restriction endonuclease (PflFI) site 5′-GACNNNGTC-3′ in twist2 and a restriction endonuclease (PvuI) site 5′-CGATCG-3′ in rpl18. c Diagram depicting the mutation associated with human DBA, mimicking the p.L51S mutation at rpl18 locus found in patients.
