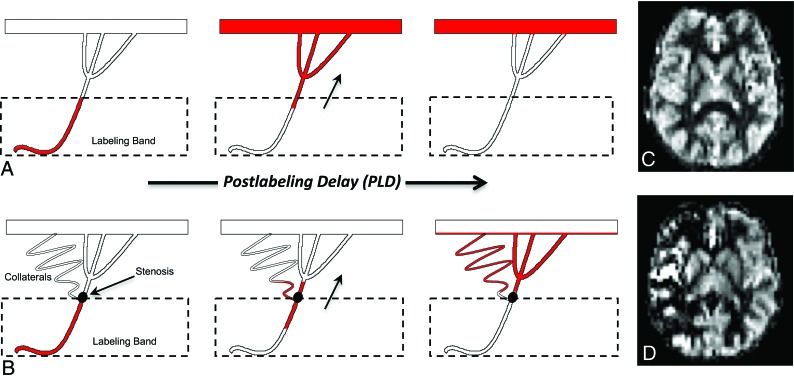
Fig 4.
Standard ASL label propagation with patent proximal vessels (A) and steno-occlusive disease with secondary collateralization (B). A, The ASL label travels from the labeling band to the distant microvasculature during the standard PLD, resulting in symmetric, homogeneous gray matter perfusion (C). B, The label is delayed due to slow flow through the stenosis and circuitous collateral pathways. Consequently, the label does not fully reach the distal microvasculture during PLD and remains caught in the macrovasculature, resulting in areas of apparent perfusion deficit and hyperintense arterial transit artifacts (D).